FDA Announces Crackdown on Kratom: What This Means for Public Health

Introduction
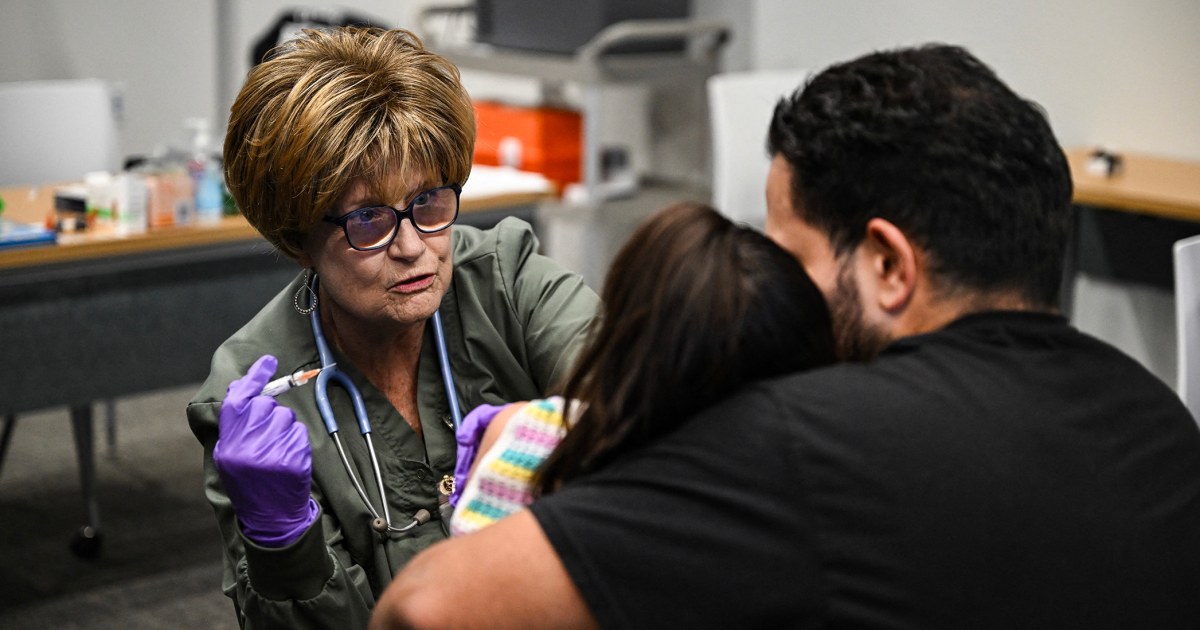
The FDA has announced a crackdown on a synthetic substance derived from kratom, a plant native to Southeast Asia. This opioid-like substance is being sold in various forms such as gummies, tablets, and drinkable shots, mainly in gas stations and convenience stores. While it is marketed as a natural and legal alternative to traditional opioids, it has raised concerns due to its potential for abuse and addiction.
The Rise of Kratom in the US
Kratom has gained popularity in the US as a natural pain reliever and mood booster. However, the FDA has not approved it for any medical use and has even issued a warning about its potential dangers. The substance is not regulated, making it difficult to ensure its safety and purity. This has led to numerous reports of adverse effects and even deaths associated with its use. The FDA's crackdown aims to address these issues and protect the public from potential harm.
The Impact of the Crackdown
The FDA's announcement is expected to have a major impact on the availability and legality of kratom in the US. It is likely that stricter regulations and enforcement will be put in place to control the sale and distribution of the substance. This will not only protect the public from potential harm, but also help in the fight against the opioid epidemic that has been plaguing the country. It is important for individuals to be aware of the risks associated with
About the Organizations Mentioned
FDA
## Overview The **U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)** is a federal agency within the Department of Health and Human Services responsible for protecting public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of a wide range of products, including human and veterinary drugs, biologics, medical devices, food, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation[1][2][3]. Its mission is to advance public health by helping to speed innovations that make medical products safer, more effective, and more affordable, while providing the public with accurate, science-based information about these products[1]. ## Functions and Regulatory Scope The FDA’s regulatory authority is expansive. It oversees the approval, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of prescription and over-the-counter drugs, vaccines, blood products, medical devices (from simple tongue depressors to complex pacemakers), dietary supplements, most foods (except some meat, poultry, and egg products regulated by the USDA), cosmetics, and tobacco products[1][2][5]. The agency also regulates electronic products that emit radiation, such as X-ray machines and microwave ovens[2][5]. Importantly, the FDA does not regulate the practice of medicine, medical services, product pricing, or health insurance reimbursement[2]. The FDA achieves its goals through a combination of **premarket reviews**, **post-market surveillance**, **facility inspections**, **enforcement actions**, and **public education**[3][4]. It maintains several adverse event reporting systems—such as MedWatch and VAERS—to monitor product safety after they reach the market[4]. The agency also plays a key role in the nation’s counterterrorism efforts by ensuring food supply security and fostering the development of medical countermeasures[1]. ## History and Key Achievements Established in 1906 with the passage of the Pure Food and Drugs Act, the FDA’s origins trace back to efforts to combat adulterated and misbranded food and drugs. Its regulatory powers expanded significantly with the