The Link Between Triclosan and Skin Problems in Children

Introduction
The use of triclosan in personal care products has been a hot topic in recent years, with concerns about its potential impact on human health. A new study conducted by the University of Michigan has found a possible link between higher levels of triclosan and skin problems in children. The findings were published in The Washington Post and have raised concerns about the safety of this common antimicrobial chemical.
Key Details
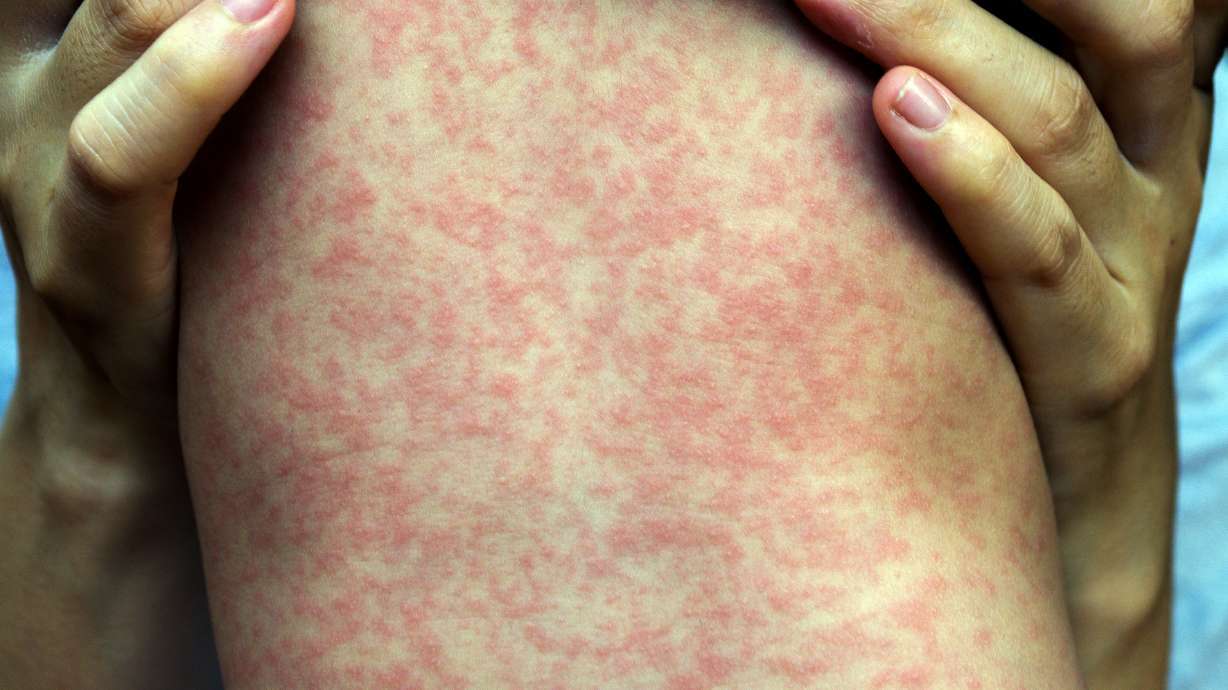
The study analyzed data from over 1000 children and found that those with higher concentrations of triclosan in their urine were 23 percent more likely to develop eczema, a common skin condition characterized by itchy and inflamed skin. This is a significant increase compared to children with lower triclosan levels. The study also found that the use of triclosan in personal care products may contribute to the development of other skin problems such as allergies and asthma.
Impact
The results of this study have raised concerns about the safety of triclosan, particularly in children. Triclosan is commonly found in products such as hand soaps, toothpaste, and deodorants, and its use is not regulated by the FDA. This means that consumers may unknowingly be exposing themselves and their children to potential health risks. With the rise of antibiotic resistance and concerns about the impact of chemicals on human health
About the Organizations Mentioned
University of Michigan
The University of Michigan, founded in 1817, is a leading public research university renowned for its academic excellence and innovative contributions. Located in Ann Arbor, Michigan, it serves over 52,000 students and employs a faculty of 8,000, making it one of the largest and most diverse institutions in the United States[1][4]. The university is a founding member of the Association of American Universities and is classified as an "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity" by the Carnegie Classification[4]. ### History and Mission Since its inception, U-M has been a national model for public higher education, focusing on research, education, and community service. Its mission is to create, communicate, preserve, and apply knowledge, fostering leaders who challenge the present and enrich the future[1]. ### Key Achievements - **Research and Rankings**: The University of Michigan ranks third among American universities in research expenditures. It has achieved numerous top rankings in various fields, including being ranked as the #1 U.S. public university by QS World University Rankings from 2019 to 2023[4][5]. - **Sustainability**: The university has successfully reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 25% ahead of its 2025 goals, reflecting its commitment to sustainability[6]. - **Innovation and Partnerships**: U-M is investing heavily in infrastructure and partnerships, such as the University of Michigan Center for Innovation in Detroit, to drive economic and educational growth[3]. ### Current Status Currently, the university is undergoing significant developments outlined in its **Campus Plan 2050** and **Vision 2034**, focusing on enhancing infrastructure, promoting sustainability, and fostering interdisciplinary research[2][3]. U-M is also expanding its presence in various regions, including Detroit and Flint, through new facilities and programs[3]. ### Notable Aspects - **Athletics**: The university's athletic teams, known as the Wolverines, compete in the Big Ten
The Washington Post
## Overview The Washington Post is a leading American daily newspaper and digital news organization based in Washington, D.C. Known for its rigorous political reporting and investigative journalism, it is widely regarded as one of the nation’s most influential newspapers, alongside The New York Times[1][2]. The Post has a significant national readership, with millions of digital subscribers and a strong presence in the Washington metropolitan area, though its print circulation has declined in recent years[1]. ## History Founded in 1877, The Washington Post initially struggled financially and editorially until financier Eugene Meyer purchased it out of bankruptcy in 1933. Under Meyer and later his daughter Katharine Graham and her husband Phil Graham, the paper expanded its influence, acquiring rival publications and building a reputation for fearless journalism[1][2]. The Post’s most famous moment came in the 1970s, when reporters Bob Woodward and Carl Bernstein uncovered the Watergate scandal, leading to the resignation of President Richard Nixon. This cemented the paper’s role as a watchdog for government accountability[1][2]. ## Key Achievements The Washington Post has won 78 Pulitzer Prizes as of 2025, the second-most of any U.S. publication[2]. Its reporting has been instrumental in major national stories, including the Pentagon Papers, secret NSA surveillance, and the January 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol[2]. The paper is also one of the few American newspapers to maintain foreign bureaus, with international news hubs in London and Seoul[1]. ## Current Status In 2013, the Graham family sold The Washington Post to Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon, for $250 million[1][2]. Under Bezos’s ownership, the paper has expanded its digital offerings and global reach. As of 2025, it has over 2.5 million digital subscribers, though print subscriptions have dipped below 100,000 for the first time in over half a
FDA
## Overview The **U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)** is a federal agency within the Department of Health and Human Services responsible for protecting public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of a wide range of products, including human and veterinary drugs, biologics, medical devices, food, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation[1][2][3]. Its mission is to advance public health by helping to speed innovations that make medical products safer, more effective, and more affordable, while providing the public with accurate, science-based information about these products[1]. ## Functions and Regulatory Scope The FDA’s regulatory authority is expansive. It oversees the approval, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of prescription and over-the-counter drugs, vaccines, blood products, medical devices (from simple tongue depressors to complex pacemakers), dietary supplements, most foods (except some meat, poultry, and egg products regulated by the USDA), cosmetics, and tobacco products[1][2][5]. The agency also regulates electronic products that emit radiation, such as X-ray machines and microwave ovens[2][5]. Importantly, the FDA does not regulate the practice of medicine, medical services, product pricing, or health insurance reimbursement[2]. The FDA achieves its goals through a combination of **premarket reviews**, **post-market surveillance**, **facility inspections**, **enforcement actions**, and **public education**[3][4]. It maintains several adverse event reporting systems—such as MedWatch and VAERS—to monitor product safety after they reach the market[4]. The agency also plays a key role in the nation’s counterterrorism efforts by ensuring food supply security and fostering the development of medical countermeasures[1]. ## History and Key Achievements Established in 1906 with the passage of the Pure Food and Drugs Act, the FDA’s origins trace back to efforts to combat adulterated and misbranded food and drugs. Its regulatory powers expanded significantly with the