Government Takes Stake in Intel for AI Race

Introduction
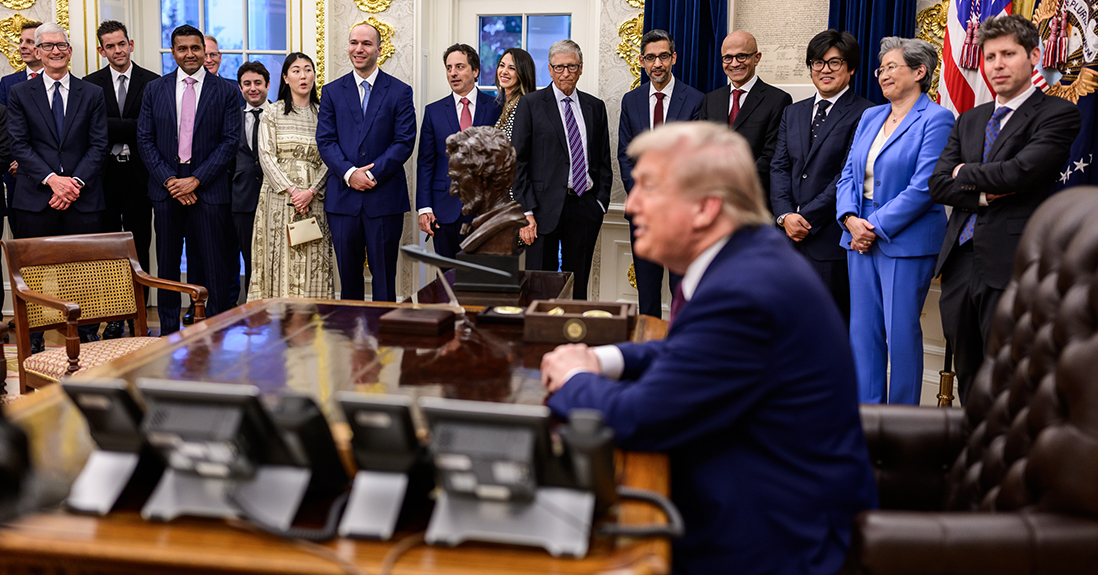
The U.S. government's decision to take a stake in Intel is a rare move that has caught the attention of many. In the past, such interventions were seen during wars or economic crises, but this time, the government's motivation has more to do with the race for AI chips and technology.
Government Interventions in the Past
The U.S. government has a history of taking stakes in American companies, especially during times of crisis. During World War II, the government took over shipbuilding companies to support the war effort, and during the 2008 financial crisis, it acquired shares in major banks to prevent them from collapsing. However, this recent intervention in Intel is unique as it is driven by the need to maintain U.S. dominance in the tech industry.
Risks and Benefits
While the government's move may seem like a positive step towards securing the country's position in the tech world, there are also potential risks involved. The government's involvement may hinder Intel's ability to make independent business decisions and could lead to conflicts of interest. On the other hand, the government's investment could also provide financial stability and resources for Intel to develop cutting-edge technology. Only time will tell how this partnership will play out and its impact on the tech race.
About the Organizations Mentioned
U.S. government
The **U.S. government** is the national governing authority of the United States, structured by the U.S. Constitution into three coequal branches: **legislative**, **executive**, and **judicial**. This tripartite system ensures a balance of power through checks and balances, preventing any single branch from becoming too powerful[1][2]. Established in 1789, its foundational framework remains in continuous effect, guiding the federal government’s operations and authority across the nation and its territories[2]. The **legislative branch**, embodied by the bicameral Congress (House of Representatives and Senate), enacts laws, controls federal spending, and provides oversight of the executive branch[2]. The **executive branch**, led by the President and supported by the Vice President, Cabinet, and federal agencies, enforces laws, manages national defense, diplomacy, and domestic policy[1][4]. The **judicial branch**, headed by the Supreme Court and lower federal courts, interprets laws and their constitutionality, ensuring legal consistency and protecting civil rights[1][2]. Historically, the U.S. government has been pivotal in shaping modern democracy, pioneering a constitutional republic that enshrines freedoms such as speech, religion, and due process through the Bill of Rights[3]. Its achievements include establishing a stable political system, advancing technology and innovation through federal initiatives, and maintaining global leadership in economic and technological sectors. Currently, the U.S. government continues to evolve, adapting to contemporary challenges like cybersecurity, digital governance, and regulatory reforms impacting business and technology. It oversees large-scale federal programs, supports innovation ecosystems, and enforces regulations affecting technology markets and privacy[6]. Notably, its structure supports a dynamic interface between federal and state powers, alongside recognition of Indigenous tribal sovereignty[2]. In business and technology contexts, the U.S. government is a major regulator, market influencer, and funder of research, maintaining transparency and accountability through public resources like Go
Intel
Intel Corporation is a leading American multinational technology company specializing in the design and manufacture of advanced semiconductors that power computing devices globally. Founded in 1968, Intel pioneered the development of microprocessors, becoming the dominant supplier of x86-based processors for PCs, servers, and other computing platforms. The company is known for its continuous innovation in semiconductor technology and its role in shaping the modern computing landscape. Intel's recent technological advancements include the launch of the Intel® Core™ Ultra series 3 processors (code-named Panther Lake) and Intel® Xeon® 6+ processors (Clearwater Forest), both built on the cutting-edge Intel 18A semiconductor node—currently the most advanced manufacturing node in the United States. These products are manufactured at Intel’s state-of-the-art Fab 52 facility in Chandler, Arizona, showcasing Intel's commitment to domestic production and technological leadership[1]. In the face of intense competition from rivals such as AMD and the architectural shifts exemplified by Apple’s move to its own silicon, Intel has been undergoing significant restructuring. This includes workforce reductions by approximately 15%, aiming to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and focus on core growth areas like AI and data centers. Financially, Intel reported solid demand and revenue resilience, with Q2 2025 revenue reaching $12.9 billion, exceeding guidance despite challenges from one-time costs and impairments[3][5]. The company is also enhancing its foundry business and AI roadmap to strengthen its competitive position and long-term shareholder value[3]. Intel’s strategic partnerships, including a $5 billion investment by Nvidia to jointly develop CPUs, and talks of adding AMD as a foundry customer, highlight its adaptive approach to industry dynamics[6]. Despite recent challenges and market shifts, Intel remains a crucial player in the semiconductor industry, advancing AI-enabled platforms and maintaining a significant impact on the global technology ecosystem[1][6].