NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Observes Interstellar Comet with Unexpected Results
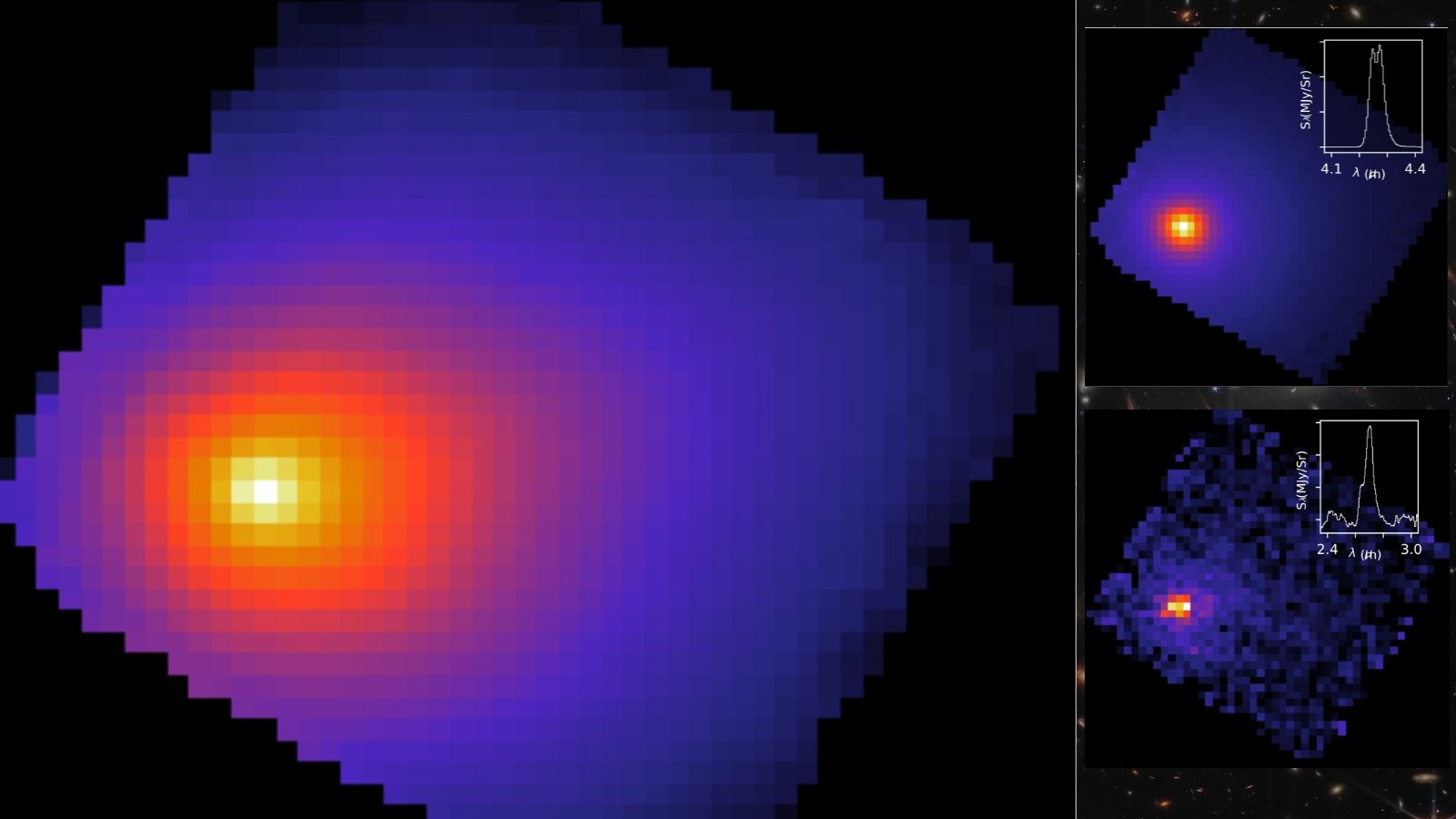
Introduction
The James Webb Space Telescope recently took its first look at the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS with unexpected results. This $10 billion space telescope, launched by NASA, has been studying the chemical contents of the comet's halo as it makes its journey through our solar system.
Key Details
The comet, which was discovered in December 2019, is only the third known interstellar object to enter our solar system. The James Webb Space Telescope was able to measure the chemical makeup of the comet's halo, including water and organic compounds. This data provides valuable insights into the composition of interstellar objects and their potential to support life.
One of the most surprising findings from the telescope's observations is the detection of carbon monoxide in the comet's halo. This suggests that the comet may have originated from a colder, outer region of its home star system. The telescope's high-resolution images also revealed intricate details of the comet's surface, giving scientists a better understanding of its structure and evolution.
Impact
The James Webb Space Telescope's study of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS has provided valuable data for scientists to further explore the mysteries of interstellar objects. This information can also help inform future missions and spacecraft designs for studying similar objects in the future. With the telescope's advanced capabilities, we can continue to unravel the mysteries