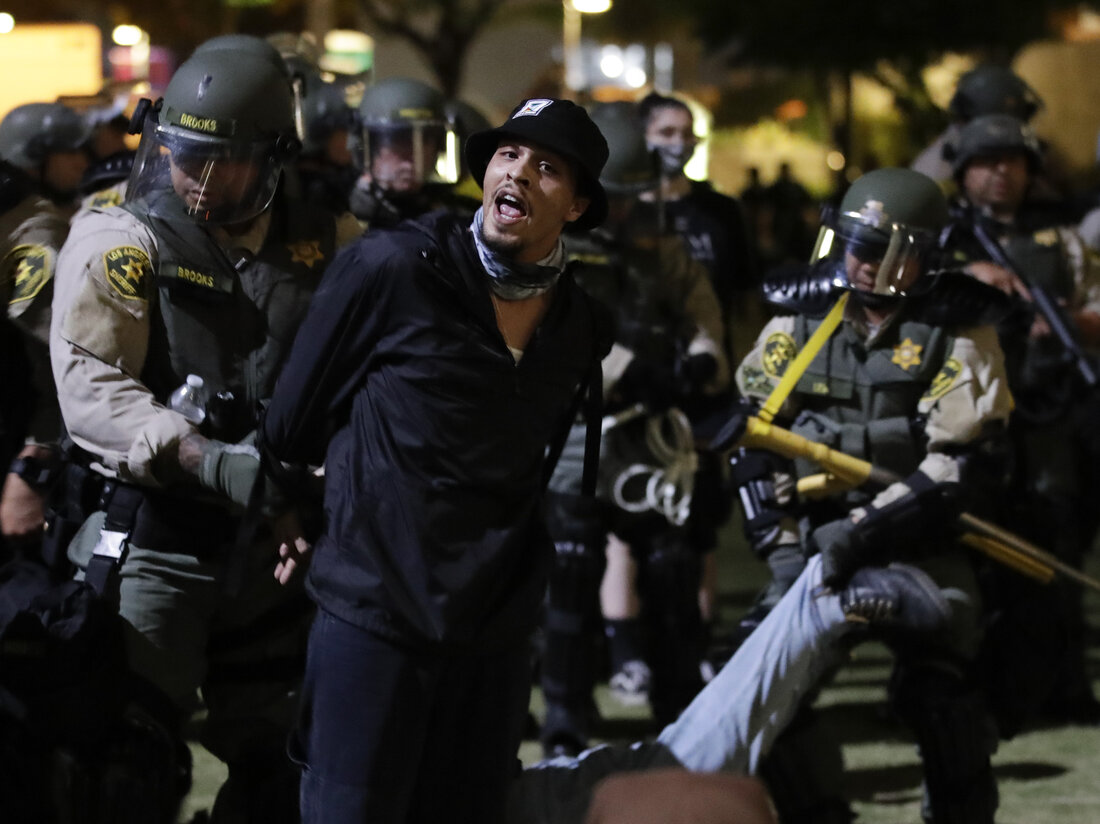Supreme Court Rules on Immigration Raids in Los Angeles
#supreme_court #immigration #los_angeles #protests #immigrant_communities

The Supreme Court Rules on Immigration Raids in the Los Angeles Area
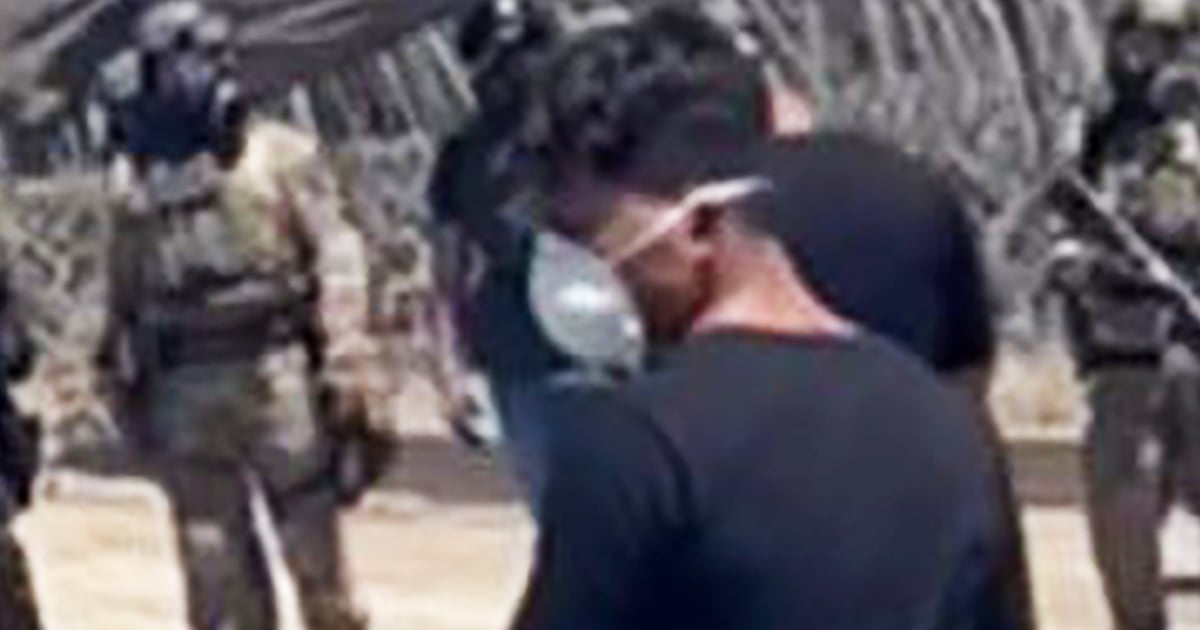
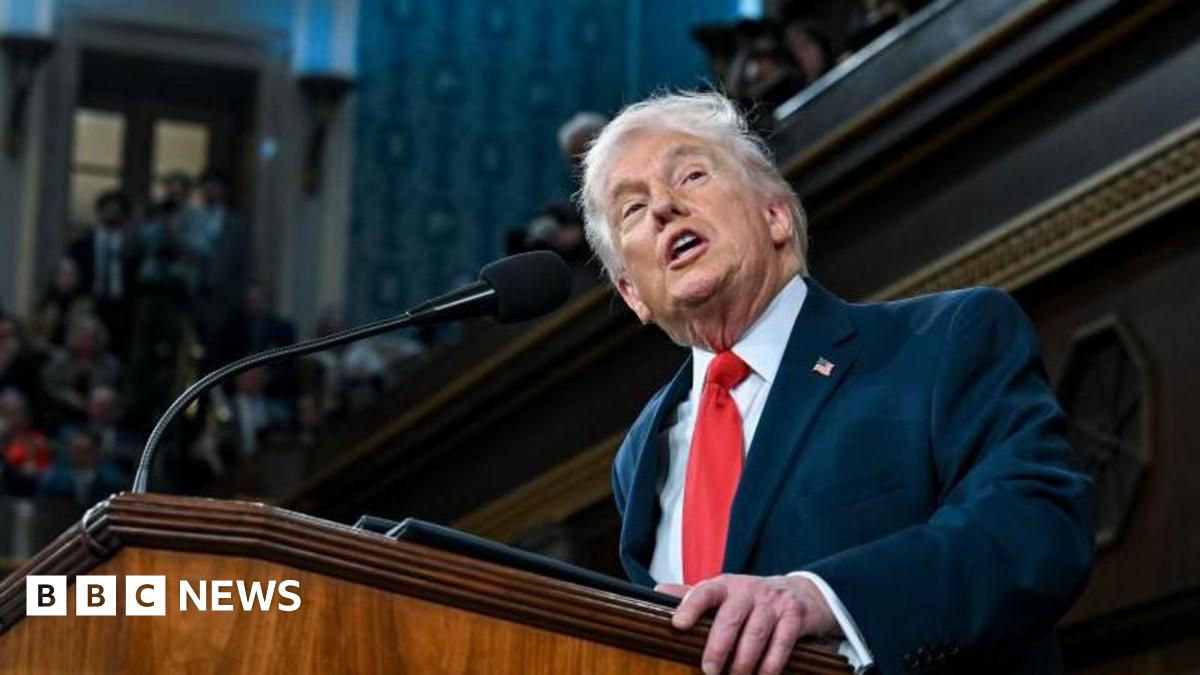
In a significant ruling, the United States Supreme Court has lifted limits on immigration raids in the Los Angeles area. This decision comes after major protests erupted in Southern California in response to these raids. President Donald Trump deployed troops from the California National Guard and Marines to assist in the raids, causing tension and further fueling the controversy surrounding the issue. The ruling has sparked concerns among immigrant communities and advocates, who fear that this decision will lead to an increase in aggressive tactics and violations of rights during these raids.
The Impact on Immigrant Communities
For years, immigrant communities in the Los Angeles area have been living in fear of these raids. The lifting of limits on these raids has only intensified their concerns and raised questions about the safety and security of their families and loved ones. Many are worried that the increased presence of military personnel in the raids will lead to more aggressive and potentially violent tactics, causing further harm and trauma to these vulnerable communities.
The Ongoing Battle for Immigration Reform
This decision by the Supreme Court is just the latest development in the ongoing battle for immigration reform. It highlights the need for comprehensive and compassionate immigration policies that prioritize the well-being and rights of individuals and families. As protests and debates continue, it is crucial for all parties to come together and find a solution that respects the
About the People Mentioned
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump, born June 14, 1946, in Queens, New York, is an American businessman, media personality, and politician. He graduated from the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School in 1968 with a degree in economics. In 1971, he took over his family’s real estate business, renaming it the Trump Organization, through which he expanded into building and managing skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. Trump gained widespread fame as the host of the reality TV show *The Apprentice* from 2004 to 2015, which helped establish his public persona as a successful entrepreneur. Trump entered politics as a Republican and was elected the 45th president of the United States, serving from 2017 to 2021. His presidency was marked by significant policy actions including tax cuts, deregulation, the appointment of three Supreme Court justices, renegotiation of trade agreements (notably replacing NAFTA with the USMCA), and a focus on immigration control including border wall expansion. He withdrew the U.S. from international agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the Iran nuclear deal, and engaged in a trade war with China. His administration’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic was criticized for downplaying the virus’s severity. Trump was impeached twice by the House of Representatives—first in 2019 for abuse of power and obstruction, and again in 2021 for incitement of insurrection—but was acquitted by the Senate both times. After losing the 2020 election to Joe Biden, Trump challenged the results, culminating in the January 6, 2021, Capitol riot. He remains a central figure in American politics, having won the 2024 presidential election and returned as the 47th president in 2025, continuing to promote policies aimed at economic growth, border security, and military strength[1][2][3][4].
About the Organizations Mentioned
California National Guard
The **California National Guard** is a dual state and federal military force comprising the California Army National Guard and the California Air National Guard, with a total strength exceeding 23,000 troops. It operates under the California Military Department and serves both the state and the United States by providing military support domestically and abroad[7][1]. The California Army National Guard (CA ARNG), a key component, consists of about 18,450 soldiers and functions as a reserve force of the U.S. Army. It uses the same ranks, training, and equipment as the regular Army and can be federalized by the President or Congress for military operations or emergencies[1][6]. The Guard’s roles include disaster relief within California—such as responses to wildfires, protests, and civil disturbances like the 1992 Los Angeles riots and June 2025 protests—and overseas military deployments supporting U.S. missions globally[1][3][5]. Historically, the California National Guard traces its lineage to militias from the California Republic era before statehood and participated alongside U.S. forces in the Mexican-American War after 1846[7]. Over time, it has evolved into a highly organized force with over 100 armories, training facilities, and aviation centers statewide[7][6]. Notably, the Guard plays a significant role in technology and business by maintaining readiness through advanced training institutes such as the 223rd Regional Training Institute and employing modern aviation and logistics capabilities[6]. Despite its achievements, the organization has faced challenges, including federal investigations into financial mismanagement[7]. Today, under the leadership of the California Adjutant General and commanders like MG Jeffrey D. Smiley, the California National Guard continues to balance its military mission with cutting-edge training and community service, making it a vital institution for both state security and national defense[6][7].
Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC) is a premier naval expeditionary force specializing in rapid response, crisis management, and sustained combat operations from both sea and land. It operates as a key component of the Department of the Navy but maintains a command structure akin to the Army, organized around Marine Expeditionary Forces (MEFs) combining ground, air, and logistics elements. This structure allows the Marines to project power globally and sustain combat operations independently for up to 60 days[2]. Historically, the Marine Corps has evolved into a highly agile and lethal force, designed to meet the demands of modern warfare. Its long-standing mission is to serve as the nation’s force in readiness, capable of responding decisively to crises worldwide. The Marine Corps Vision and Strategy 2025 outlines its future orientation—emphasizing multicapable Marine Air-Ground Task Forces (MAGTFs) that are mission-tailored, expeditionary, and optimized for naval operations. The strategy highlights modernization efforts focused on advanced equipment, logistics, and battlefield adaptability to maintain strategic freedom and operational flexibility against emerging threats[1]. Recent organizational changes include reverting infantry squads to 13 Marines to optimize combat effectiveness and creating a new reconnaissance and fires company within infantry battalions to incorporate drones, mortars, and other precision fires. These adjustments reflect the Corps’ focus on integrating technology and enhancing battlefield lethality[4]. The Marine Corps is also undergoing a comprehensive modernization plan, incorporating new aircraft like the F-35B and F-35C to maintain air superiority and support from the skies. This modernization is balanced with a commitment to training, deployment, and retention amid recruiting challenges. The Corps emphasizes readiness and presence, particularly in strategic regions like Korea, the Philippines, and Australia, to uphold its rapid deployment capability[5][8]. Overall, the USMC remains a critical, technology-driven force in national defense, continuously adapting its structure, equipment, and strategies to meet 21s