Unveiling 3I/ATLAS Jet Structures: Insights into Interstellar Comets
#interstellar #comets #jet_structure #observations #astrophysics
Introduction to 3I/ATLAS’ Jet Structure
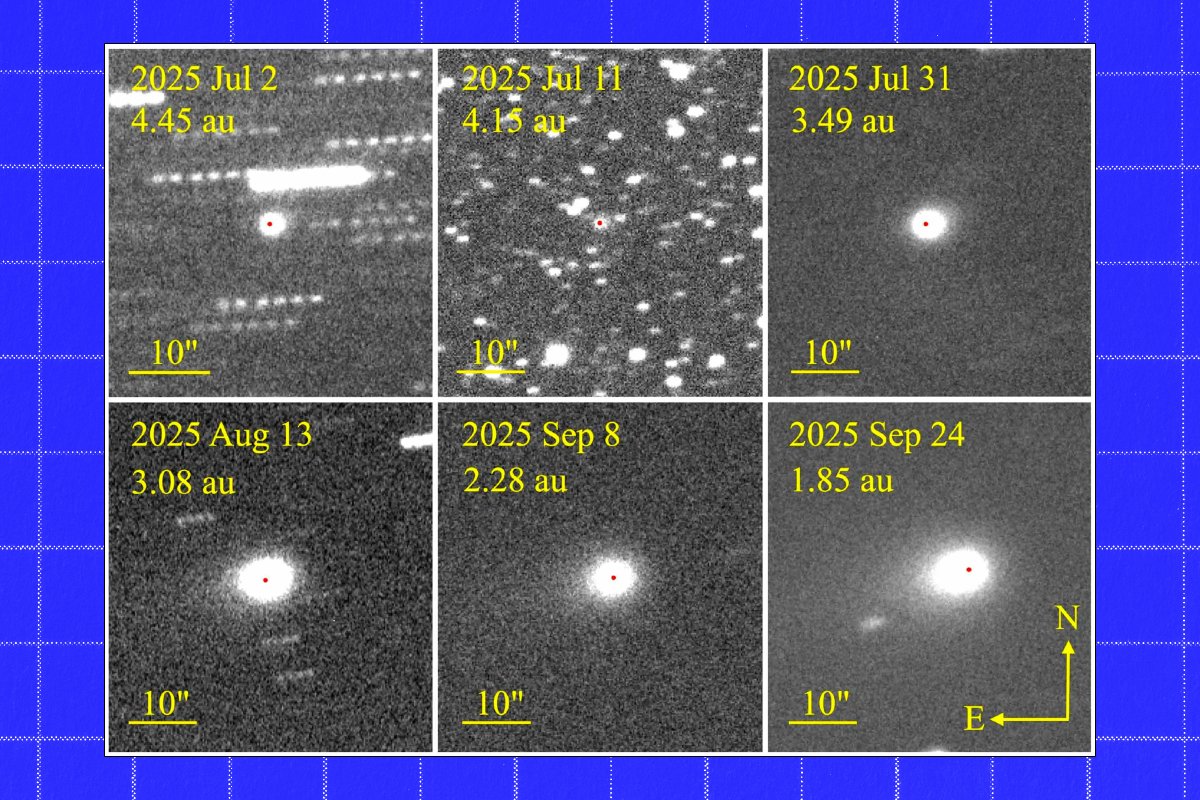
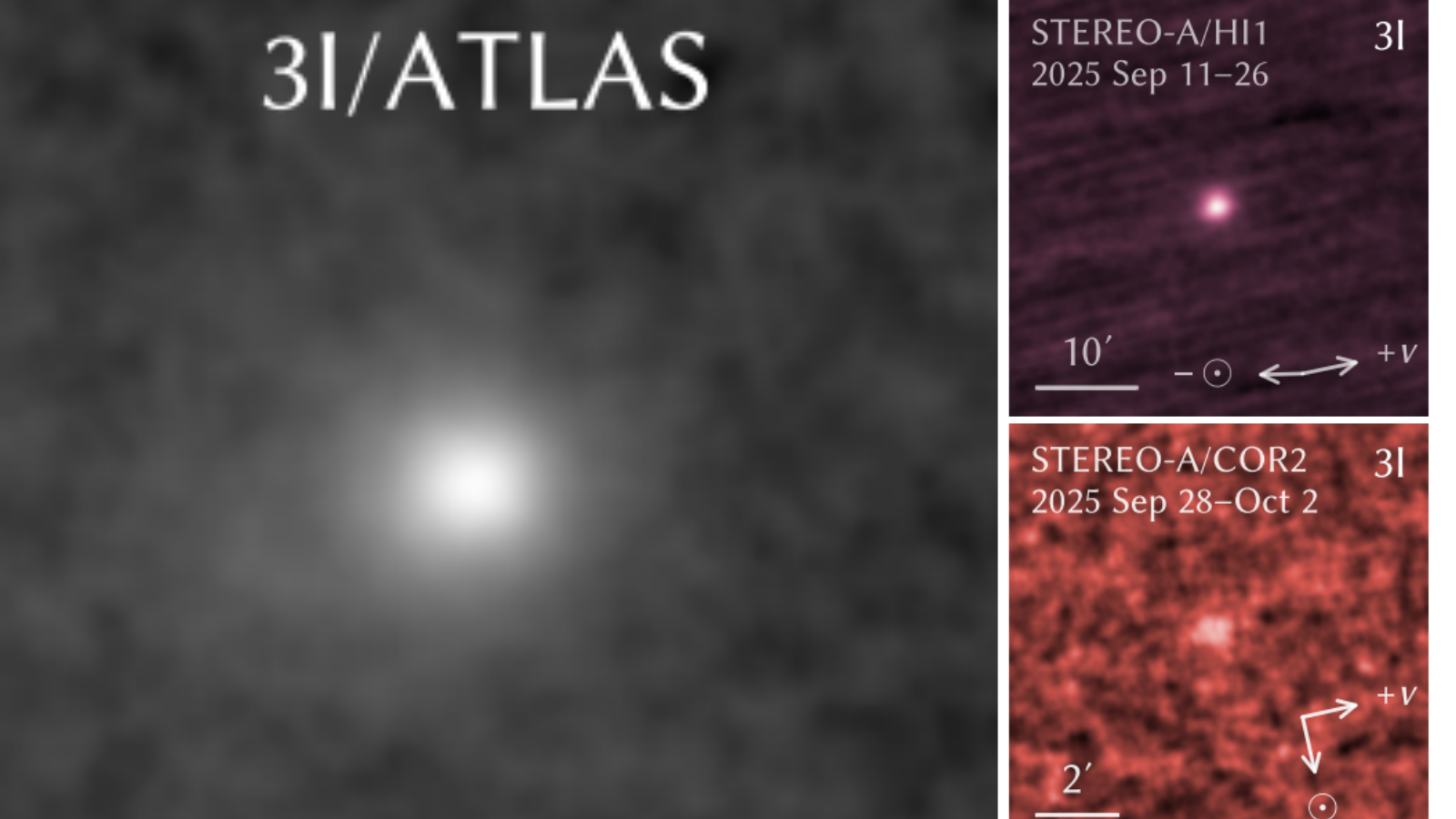
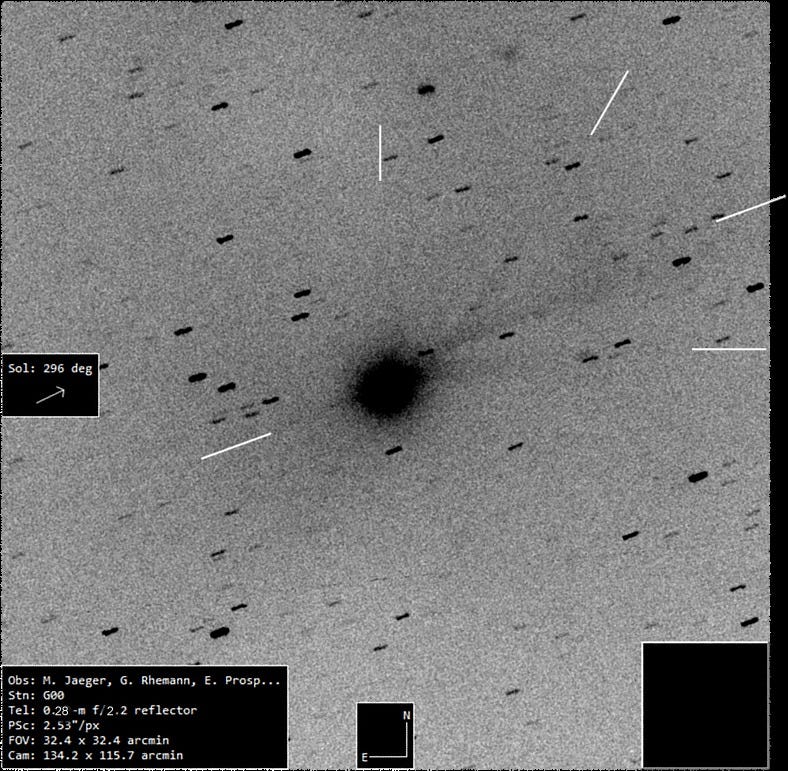
On November 8, 2025, at 4:10 Universal Time, the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS exhibited a remarkable and intricate jet structure shortly after its perihelion passage. This phenomenon marks a significant observation in the study of interstellar comets, showcasing dynamic material ejections that challenge previous assumptions about such objects. The complex jets suggest active processes on or near the comet’s surface, possibly driven by sublimation of volatile materials.
Observational Significance
The discovery of 3I/ATLAS’ jet structure provides valuable insights into the physical properties and behavior of interstellar visitors. Unlike typical solar system comets, 3I/ATLAS’ jets display multiple streams of dust and gas, indicating heterogeneous surface activity. These findings contribute to understanding of how such objects interact with solar radiation and gravitational forces during close solar approaches. Researchers like M. Jäger emphasize the importance of detailed monitoring to track evolving jet morphology over time.
Implications for Interstellar Studies
This complex jet activity not only enriches cometary science but also opens new avenues for exploring the composition and origin of interstellar objects. By analyzing jet emissions, scientists can infer chemical makeup and thermal properties, improving models of interstellar medium interactions. The observation of 3I/ATLAS’ jets thus represents a milestone, suggesting that interstellar comets may harbor diverse and active environments beyond our solar system.