Debate over Vaccines and Health
Introduction
The CDC's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices held a meeting on Thursday to discuss and vote on the hepatitis B and measles, mumps, rubella and varicella (MMRV) vaccines for children. This comes as the committee welcomed new members, hand-picked by Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a vocal anti-vaccine advocate and the son of the late Senator Robert F. Kennedy.
Vaccine Safety Debate
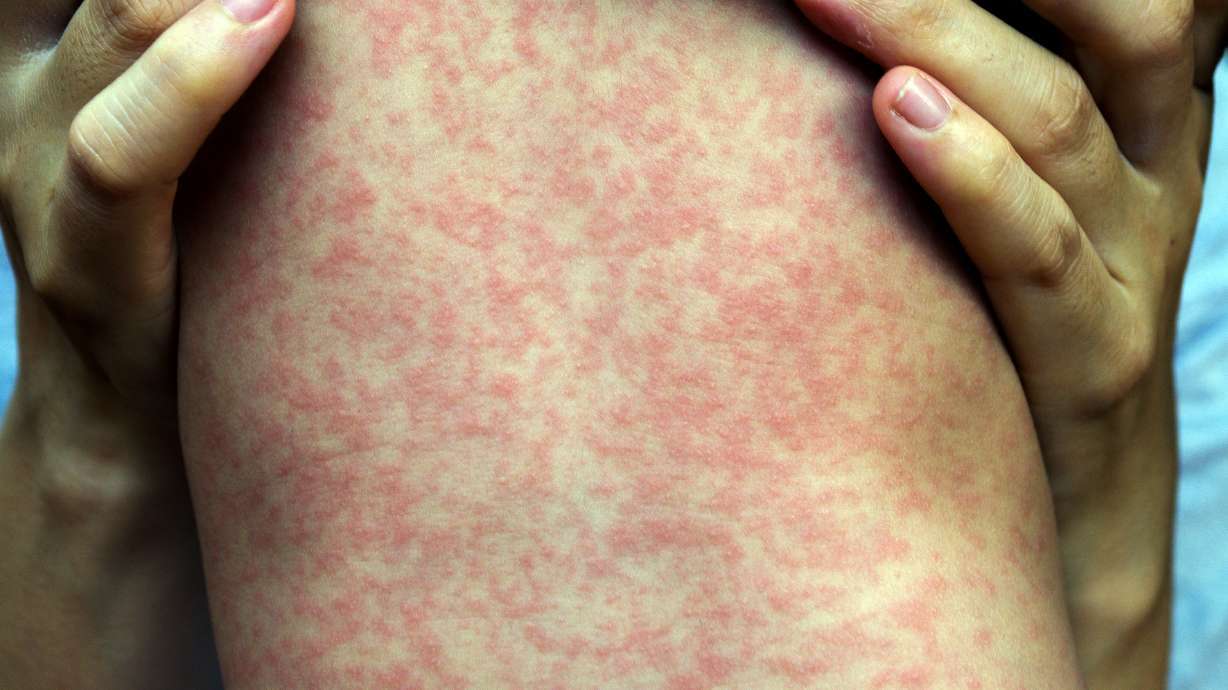
The discussion surrounding the safety of vaccines has been ongoing, with some parents and activists raising concerns about potential side effects and adverse reactions. This has led to a decline in vaccination rates in some areas, which has resulted in outbreaks of preventable diseases like measles. However, according to the CDC, vaccines are rigorously tested and monitored for safety and continue to be one of the most effective ways to prevent and control infectious diseases.
The Importance of Vaccines
The CDC's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices plays a crucial role in determining the recommended vaccine schedule for children. This schedule is based on extensive research and balancing the risks and benefits of each vaccine. Vaccines not only protect the individual who receives them, but also contribute to herd immunity, protecting those who cannot receive vaccines due to medical reasons. It is important to trust the recommendations of medical experts and make informed decisions about vaccinations.
About the People Mentioned
Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. is an American politician, environmental lawyer, and author, born on January 17, 1954, in Washington, D.C. He is the third of eleven children of Robert F. Kennedy, the U.S. Attorney General, and Ethel Skakel Kennedy. His family's political legacy includes his uncle, President John F. Kennedy. Kennedy's early life was marked by personal struggles, including drug addiction, which led to his arrest for heroin possession in 1983. However, he later redirected his life towards environmental advocacy and public service. Kennedy graduated from Harvard University in 1976 with a degree in American history and literature and later earned a law degree from the University of Virginia in 1981. He began his career as an assistant district attorney in Manhattan but soon shifted his focus to environmental law. In 1987, he received a master's degree in environmental law from Pace University, where he taught environmental law from 1986 to 2018 and co-founded the Environmental Litigation Clinic. Notably, Kennedy is the founder of the Waterkeeper Alliance, a global clean water advocacy group, and Children's Health Defense, which focuses on childhood chronic diseases and environmental exposures. He has been recognized for his environmental activism, including being named TIME Magazine's "Hero for the Planet" for his efforts in restoring the Hudson River. Kennedy has also been involved in high-profile legal cases against companies like DuPont and Monsanto. In recent years, he has been a vocal figure in vaccine skepticism and public health controversies. In the 2024 U.S. presidential election, Kennedy initially ran as an independent candidate before endorsing Donald Trump. Currently, his involvement in public life includes controversial stances on health and environmental issues. Despite these controversies, his work in environmental law and advocacy has had significant impacts on public health and environmental protection.
About the Organizations Mentioned
CDC
The **Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)** is the premier national public health agency of the United States, operating under the Department of Health and Human Services and headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. Its primary mission is to protect public health and safety through disease control, injury prevention, and health promotion both nationally and globally[1][8]. Established in 1946 initially as a single "Center for Disease Control," the agency expanded and reorganized in 1980 into multiple specialized centers, reflecting a broader focus beyond infectious diseases to include environmental health, chronic disease, occupational safety, and health education[7]. The CDC comprises various centers and institutes, such as the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), among others. These centers enable the CDC to address a wide array of public health challenges through research, surveillance, policy development, and education[2]. It also plays a key role in emergency preparedness and response, demonstrated notably during the COVID-19 pandemic, where its guidance shaped public health actions despite complex political and social dynamics[8]. Key achievements include pioneering epidemiological research, controlling outbreaks of infectious diseases, advancing vaccine safety and immunization programs, and addressing emerging health threats such as obesity and diabetes. The CDC is recognized for disseminating authoritative health information, including the widely cited Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), and for its global collaborations with health organizations worldwide[1][3][8]. Currently, the CDC is undergoing organizational adjustments to focus more intensively on infectious diseases, as part of the 2025 Department of Health and Human Services reorganization. This includes absorbing the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response while shifting some functions like occupational safety to new entities[1]. The agency’s comprehensive approach, backed by science and government funding, positions it as a critical leader in public health innovation, disease prevention, and health security i
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
## Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP): Overview, History, and Impact The **Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)** is a federal advisory committee under the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) responsible for providing expert recommendations on the use of vaccines and related agents to control vaccine-preventable diseases in the U.S. civilian population[1][2][6]. Its guidance covers routine immunization schedules for children and adults, as well as nonroutine situations such as outbreaks and travel[2]. ACIP’s recommendations are foundational for both public health policy and clinical practice, influencing everything from school entry requirements to insurance coverage for vaccines[1]. ## History and Structure Established in March 1964 by the U.S. Surgeon General, ACIP was created under Section 222 of the Public Health Service Act to provide ongoing, independent advice to the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) on vaccine policy[1][2]. The committee comprises medical and public health experts, including both voting and liaison members, and operates through regular public meetings and specialized work groups that review evidence and draft recommendations[2][6]. Final recommendations require a majority vote and are published in CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), making them official federal guidance[1][2]. ## Key Achievements ACIP’s recommendations have shaped the U.S. immunization landscape for over half a century, ensuring the integration of new vaccines (such as those for HPV, hepatitis B, and COVID-19) into routine care as soon as they are licensed[1][2]. During the COVID-19 pandemic, ACIP played a pivotal role in rapidly developing and updating vaccination guidelines, including recommendations for multiple age groups and immunocompromised individuals[5]. The committee’s rigorous, evidence-based process is designed to balance scientific rigor with public transparency, often assessing new vaccines in parallel with FDA approval[7]. ## Current Status