The Impact of Inflation Data on the Stock Market
Stock Market Today: S&P 500 Falls a Second Day - Barron's
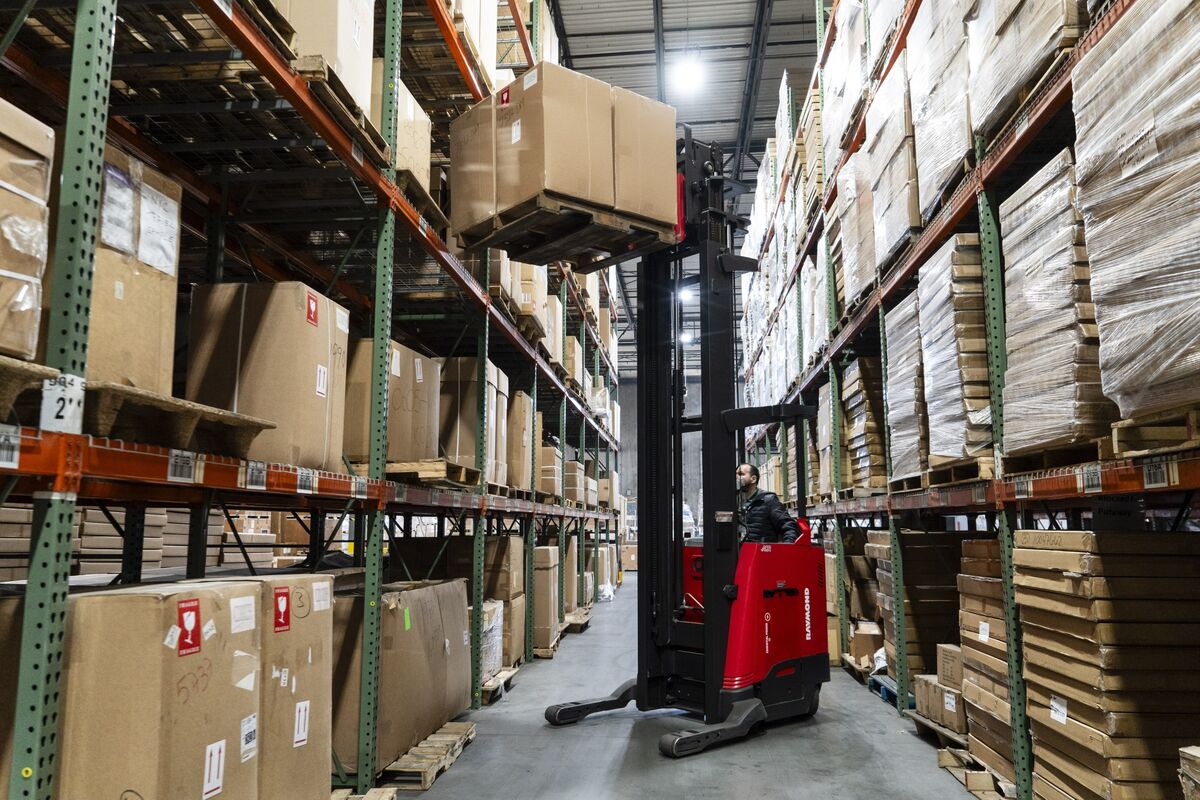
The stock market saw a second consecutive day of decline as the Dow, S&P 500, and Nasdaq all fell. This downward trend was driven by Wall Street's anticipation of the upcoming inflation data. Analysts and investors alike are closely monitoring the data, as rising inflation could have a significant impact on the market's performance.
Inflation Data and its Effects
The anticipation of inflation data has sparked concerns among investors, as higher inflation could lead to a decrease in consumer spending and slower economic growth. This could ultimately lead to a decrease in corporate profits and a potential dip in stock prices. Inflation has been a hot topic in recent months, with the Federal Reserve keeping a close eye on rising prices and their potential impact on the economy.
Investor Sentiment and Future Outlook
The recent decline in the stock market has caused some worry among investors, but it's important to keep in mind that market fluctuations are a natural part of investing. The volatility seen in the market today may be temporary, and it's crucial for investors to maintain a long-term perspective. As we await the inflation data, it's important for investors to stay informed and make well-informed decisions based on their risk tolerance and investment goals.
About the Organizations Mentioned
Federal Reserve
## Overview and Mission The Federal Reserve, often called the "Fed," is the central bank of the United States, established by Congress in 1913 to provide the nation with a safer, more flexible, and stable monetary and financial system[1]. Its mission centers on a dual mandate from Congress: to promote maximum employment and maintain price stability, ensuring the dollar retains its value over time[1]. The Fed operates through a unique hybrid structure, combining a national Board of Governors in Washington, D.C., with 12 independent regional Reserve Banks, including institutions like the Cleveland Fed[1]. This decentralized setup allows the Fed to closely monitor economic conditions across diverse regions, industries, and communities, while maintaining independence from short-term political influences[1]. ## Key Functions The Fed’s responsibilities are broad and vital to the U.S. economy. It conducts monetary policy—primarily by influencing interest rates—to achieve its employment and inflation goals[2]. The Fed also supervises and regulates banks to ensure the safety and soundness of the financial system, works to minimize systemic risks, and fosters efficient payment and settlement systems[2]. Additionally, it promotes consumer protection and community development, addressing emerging issues through research, supervision, and enforcement of consumer laws[2]. ## History and Evolution The Federal Reserve is the third central bank in U.S. history, following two failed attempts in the 19th century[1]. Its creation was a response to the financial turbulence of the early 20th century, aiming to prevent crises and stabilize the economy. Over time, the Fed has evolved, adopting more transparent and inclusive policymaking processes. For example, it now conducts regular reviews of its monetary policy framework, engaging with academics, businesses, and the public to refine its strategies and communications[3][5]. ## Recent Developments and Achievements In 2025, the Fed completed its second major review of its monetary policy strategy, tools, and communications, reaffirming its commitment to transparenc














