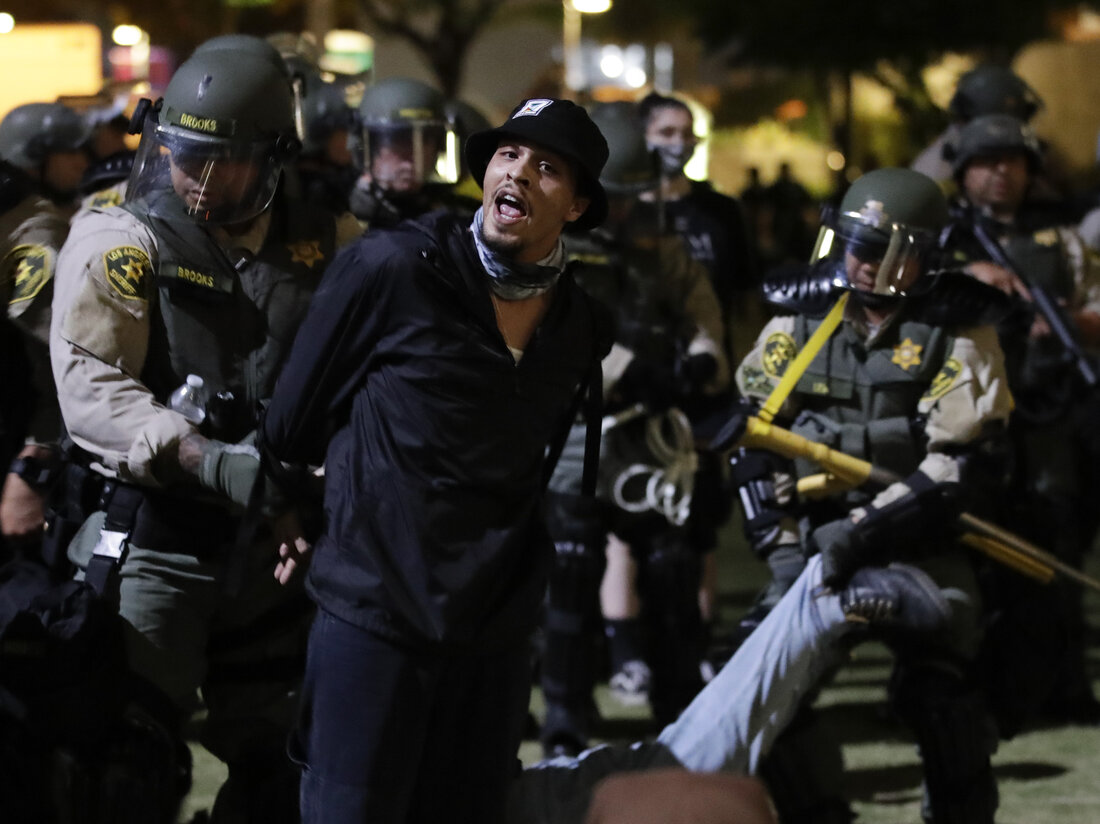Proposed Cuts to NPR, PBS and Foreign Aid Aim to Reduce Federal Deficit

About the People Mentioned
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump, born June 14, 1946, in Queens, New York, is an American businessman, media personality, and politician. He graduated from the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School in 1968 with a degree in economics. In 1971, he took over his family’s real estate business, renaming it the Trump Organization, through which he expanded into building and managing skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. Trump gained widespread fame as the host of the reality TV show *The Apprentice* from 2004 to 2015, which helped establish his public persona as a successful entrepreneur. Trump entered politics as a Republican and was elected the 45th president of the United States, serving from 2017 to 2021. His presidency was marked by significant policy actions including tax cuts, deregulation, the appointment of three Supreme Court justices, renegotiation of trade agreements (notably replacing NAFTA with the USMCA), and a focus on immigration control including border wall expansion. He withdrew the U.S. from international agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the Iran nuclear deal, and engaged in a trade war with China. His administration’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic was criticized for downplaying the virus’s severity. Trump was impeached twice by the House of Representatives—first in 2019 for abuse of power and obstruction, and again in 2021 for incitement of insurrection—but was acquitted by the Senate both times. After losing the 2020 election to Joe Biden, Trump challenged the results, culminating in the January 6, 2021, Capitol riot. He remains a central figure in American politics, having won the 2024 presidential election and returned as the 47th president in 2025, continuing to promote policies aimed at economic growth, border security, and military strength[1][2][3][4].
About the Organizations Mentioned
NPR
National Public Radio (NPR) is a premier American public broadcasting organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with NPR West based in Culver City, California. It functions primarily as a national syndicator, distributing content to a network of over 1,000 public radio stations across the United States, most of which are owned by non-profit entities such as public school districts, colleges, and universities[1]. Founded in 1970, NPR operates independently of government or corporate control, relying financially on dues and fees from member stations, corporate underwriting, and grants from the publicly funded Corporation for Public Broadcasting. This financial model helps maintain its editorial independence and diverse programming[1]. NPR is best known for its flagship news programs, *Morning Edition* and *All Things Considered*, which are among the most popular drive-time radio shows nationally, attracting weekly audiences of approximately 15 million each. These programs exemplify NPR’s strong reputation for in-depth, factual, and engaging news coverage, appealing to listeners interested in business, technology, and broader cultural topics[1]. Beyond radio, NPR manages the Public Radio Satellite System, which distributes not only its own programming but also content from independent producers and networks like American Public Media and Public Radio Exchange (PRX). It also serves as a primary entry point for the Emergency Alert System. NPR content is widely accessible on demand via online streaming, mobile apps, and podcasts, reflecting its strategic adaptation to digital media trends and the growing podcast market[1][2]. Notable aspects of NPR include its commitment to innovation in public media and its collaboration with leading organizations to navigate challenges such as historic federal funding cuts. NPR’s role in shaping public discourse through trusted journalism and storytelling makes it a vital institution in the U.S. media landscape, especially for audiences focused on business and technology news[1][2].
PBS
## Overview The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is a non-profit public television network in the United States, renowned for its educational, cultural, and news programming. PBS operates as a consortium of member stations, providing high-quality content free from commercial interruptions, with a mission to inform, educate, and inspire the American public[2][5]. ## History PBS was established on November 3, 1969, by a group of broadcasters and educators, including Hartford N. Gunn Jr., John Macy, James Day, and Kenneth A. Christiansen, following recommendations from the Carnegie Commission on Public Television[2][1]. It officially launched operations on October 5, 1970, succeeding the National Educational Television (NET) network[1][2]. The creation of PBS was a response to the growing demand for a federally supported public television system that could coordinate funding and distribute programming nationally[1][2]. ## What PBS Does PBS’s primary function is to distribute programming to its member stations across the country. Its content spans children’s education (e.g., *Sesame Street*, *Mister Rogers’ Neighborhood*), drama (*Masterpiece Theatre*), science (*NOVA*), news and public affairs (*PBS NewsHour*), documentaries (including those by Ken Burns), and cultural programs (*Live from Lincoln Center*)[1][3][5]. PBS is also known for its commitment to diversity, inclusion, and addressing social issues through its programming[1]. ## Key Achievements PBS has been instrumental in transforming American television by pioneering educational and cultural programming. Its children’s shows, such as *Sesame Street*, have won numerous awards and are credited with advancing early childhood education[1][3]. The network’s coverage of major national events, like the Watergate hearings, demonstrated its capacity for in-depth, public service journalism[2]. PBS has also introduced American audiences to acclaimed international content, including