CDC Shooting: Misinformation and Its Dangerous Consequences

Introduction
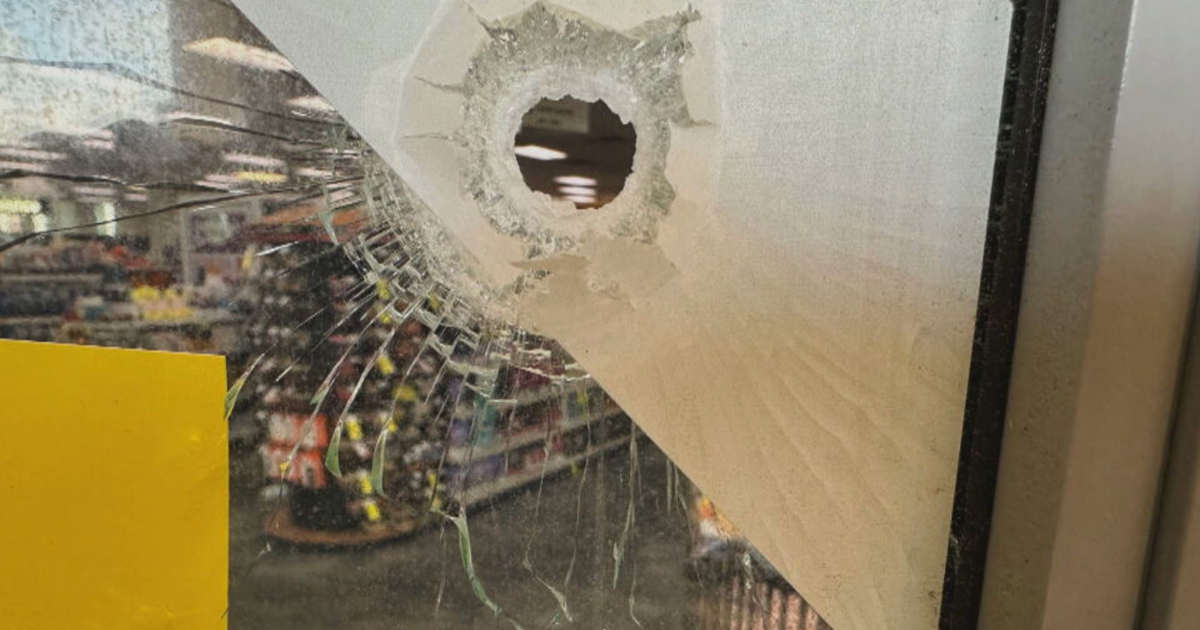
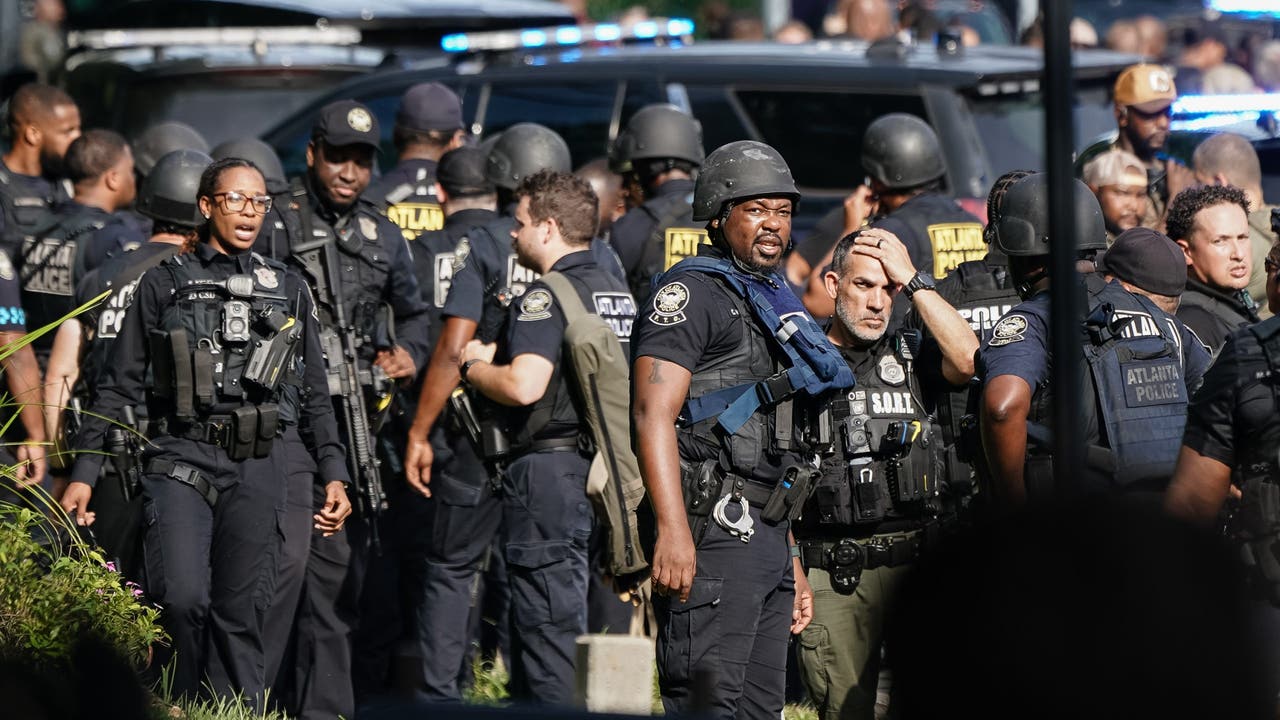
The recent shooting at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has left many people shocked and angry. According to two CDC officials briefed on the case, investigators believe that the shooter targeted the agency due to his beliefs about the coronavirus vaccine. But his anger is not just directed at the CDC. In the aftermath of the shooting, employees are turning their frustration towards Robert F. Kennedy Jr. and President Donald Trump.
Key Details
Kennedy, a well-known anti-vaccine activist, has been spreading misinformation about the COVID-19 vaccine and its potential dangers. He has also been a vocal critic of the CDC and its handling of the pandemic. As a result, many employees at the agency feel that Kennedy's rhetoric has contributed to the hostile environment that led to the shooting. Furthermore, President Trump has also been accused of fueling anti-vaccine sentiments with his own statements and actions.
Impact
This tragic event highlights the dangerous consequences of spreading false information and sowing doubt about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines. It also sheds light on the growing divide between those who believe in science and those who reject it. The shooting has left the CDC community in shock and mourning, but it has also served as a wake-up call to address the dangers of misinformation and the need for responsible and evidence-based communication.
About the People Mentioned
Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. is an American politician, environmental lawyer, and author, born on January 17, 1954, in Washington, D.C. He is the third of eleven children of Robert F. Kennedy, the U.S. Attorney General, and Ethel Skakel Kennedy. His family's political legacy includes his uncle, President John F. Kennedy. Kennedy's early life was marked by personal struggles, including drug addiction, which led to his arrest for heroin possession in 1983. However, he later redirected his life towards environmental advocacy and public service. Kennedy graduated from Harvard University in 1976 with a degree in American history and literature and later earned a law degree from the University of Virginia in 1981. He began his career as an assistant district attorney in Manhattan but soon shifted his focus to environmental law. In 1987, he received a master's degree in environmental law from Pace University, where he taught environmental law from 1986 to 2018 and co-founded the Environmental Litigation Clinic. Notably, Kennedy is the founder of the Waterkeeper Alliance, a global clean water advocacy group, and Children's Health Defense, which focuses on childhood chronic diseases and environmental exposures. He has been recognized for his environmental activism, including being named TIME Magazine's "Hero for the Planet" for his efforts in restoring the Hudson River. Kennedy has also been involved in high-profile legal cases against companies like DuPont and Monsanto. In recent years, he has been a vocal figure in vaccine skepticism and public health controversies. In the 2024 U.S. presidential election, Kennedy initially ran as an independent candidate before endorsing Donald Trump. Currently, his involvement in public life includes controversial stances on health and environmental issues. Despite these controversies, his work in environmental law and advocacy has had significant impacts on public health and environmental protection.
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump, born June 14, 1946, in Queens, New York, is an American businessman, media personality, and politician. He graduated from the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School in 1968 with a degree in economics. In 1971, he took over his family’s real estate business, renaming it the Trump Organization, through which he expanded into building and managing skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. Trump gained widespread fame as the host of the reality TV show *The Apprentice* from 2004 to 2015, which helped establish his public persona as a successful entrepreneur. Trump entered politics as a Republican and was elected the 45th president of the United States, serving from 2017 to 2021. His presidency was marked by significant policy actions including tax cuts, deregulation, the appointment of three Supreme Court justices, renegotiation of trade agreements (notably replacing NAFTA with the USMCA), and a focus on immigration control including border wall expansion. He withdrew the U.S. from international agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the Iran nuclear deal, and engaged in a trade war with China. His administration’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic was criticized for downplaying the virus’s severity. Trump was impeached twice by the House of Representatives—first in 2019 for abuse of power and obstruction, and again in 2021 for incitement of insurrection—but was acquitted by the Senate both times. After losing the 2020 election to Joe Biden, Trump challenged the results, culminating in the January 6, 2021, Capitol riot. He remains a central figure in American politics, having won the 2024 presidential election and returned as the 47th president in 2025, continuing to promote policies aimed at economic growth, border security, and military strength[1][2][3][4].
About the Organizations Mentioned
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is a premier U.S. public health agency established on July 1, 1946, originally as the Communicable Disease Center. It evolved from the wartime Malaria Control in War Areas program (MCWA) created during World War II to combat malaria around military bases in the southern United States[1][3][7]. Headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, the CDC has grown from a regional malaria control unit to a comprehensive national and global health protection agency. The CDC’s mission is to protect public health and safety through disease control and prevention, health promotion, and emergency preparedness. It investigates and responds to emerging health threats such as infectious diseases—including COVID-19, influenza, and bioterrorism agents—as well as chronic diseases, injuries, workplace hazards, environmental health threats, and more[2][6]. The agency conducts scientific research via over 200 specialized laboratories nationwide, supports public health workforce development, and communicates critical health information to the public[6][5]. Throughout its history, the CDC has expanded its scope and structure significantly. It was renamed the Center for Disease Control in 1970, then the Centers for Disease Control in 1980 as it incorporated multiple centers, and finally adopted the current name, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 1992 to emphasize prevention efforts while retaining the CDC acronym for recognition[2][8]. Its organizational breadth now includes centers focused on infectious diseases, chronic diseases, environmental health, injury prevention, occupational safety, and health statistics. Notable achievements include leading vaccination campaigns against diseases like measles and rubella, advancing injury prevention, and mounting global efforts against infectious outbreaks. The CDC also played a pivotal role in combating antibiotic misuse and bioterrorism preparedness. Despite past controversies like the Tuskegee syphilis study, the agency remains a leader in epidemiology and public health innovation, employing a multidisciplinary workforce of scientists, clinicians, and public health experts dedicated t