UN to Recognize Palestine as a State

Introduction
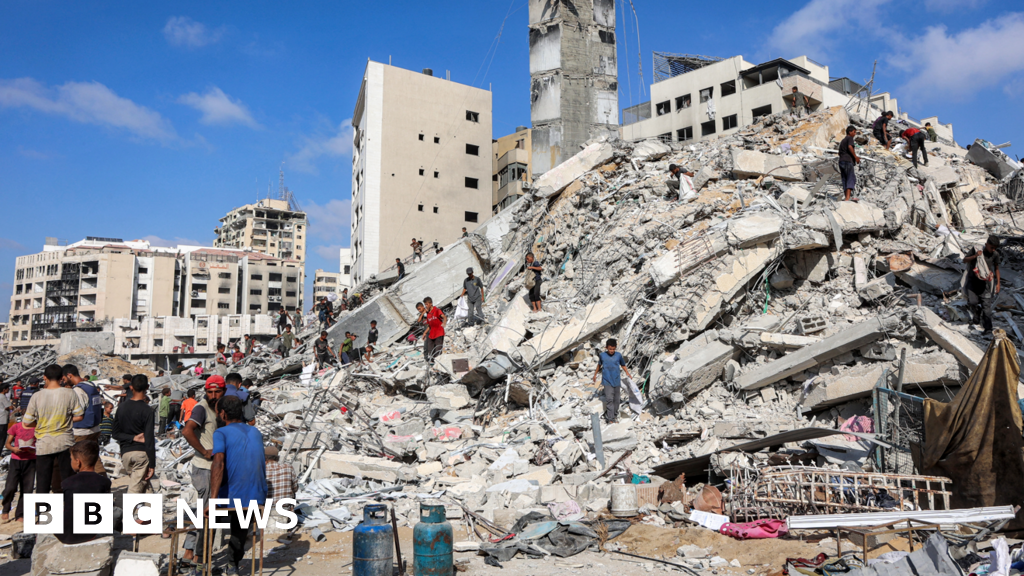
In a move that has sparked controversy and debate, several European countries have announced their intention to recognize Palestine as a state at the United Nations. While this may seem like a symbolic gesture, it has significant implications for the ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine. Israel and its allies have condemned this decision, calling it "political theater." On the other hand, supporters of Palestinian rights see this as a crucial first step towards achieving justice and self-determination for the Palestinian people.
Key Details
The recognition of Palestine as a state would grant the country more legitimacy on the global stage and could potentially open doors for diplomatic negotiations. It would also give Palestinians the opportunity to bring their grievances to international bodies, such as the International Criminal Court. This could hold Israel accountable for any human rights abuses and violations of international law. Moreover, formal recognition would also provide Palestinians with a sense of national identity and give them a stronger voice in the international community.
Impact
The decision to recognize Palestine as a state has the potential to tilt the power dynamics in the region. It could put pressure on Israel to come to the negotiating table and make concessions for a lasting peace. However, it could also lead to further tensions and backlash from Israel and its allies. It remains to be seen how this move will impact the already fragile relationship between Israel and Palestine. One thing is certain, though –
About the Organizations Mentioned
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is a pivotal international organization established in 1945, following the devastation of World War II, with the primary goal of maintaining global peace and security, fostering international cooperation, and promoting social progress. The UN Charter, signed by 51 founding member states, including the United States, the United Kingdom, China, and the Soviet Union, laid the foundation for this ambitious endeavor[1][3]. ## History and Structure The UN was born out of the failures of its predecessor, the League of Nations, which failed to prevent World War II. Key planning meetings, such as the Dumbarton Oaks Conference in 1944, defined the UN's structure, which includes the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat[1][6]. The Security Council, with five permanent members (the United States, China, France, Russia, and the United Kingdom), holds significant influence due to its veto power[2]. ## Key Achievements Over the years, the UN has played a crucial role in conflict resolution, human rights advocacy, and sustainable development. Notable achievements include the establishment of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948 and the implementation of numerous peacekeeping missions worldwide[3][4]. The UN has also been instrumental in addressing global challenges such as climate change and pandemics through its various programs and agencies. ## Current Status Today, the UN comprises 193 member states, with its most recent addition being South Sudan in 2011[5]. The organization continues to evolve, addressing emerging issues like digital governance and cybersecurity. Despite challenges, the UN remains a cornerstone of international diplomacy and cooperation. ## Notable Aspects The UN's work is not limited to politics; it also impacts business and technology through initiatives that promote sustainable development and digital inclusion. Its role in setting global standards and fostering international cooperation makes it a significant player in shaping the
International Criminal Court
The **International Criminal Court (ICC)** is a permanent international tribunal established to prosecute individuals responsible for the most serious crimes under international law: **genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression**[2][4]. It operates independently of the United Nations but collaborates with it, particularly in investigations and security matters[2][6]. Founded by the **Rome Statute** in 1998 and operational since 2002, the ICC aims to end impunity for grave offenses that national courts are unable or unwilling to prosecute[1][2][7]. Located in **The Hague, Netherlands**, the ICC investigates, prosecutes, and tries individuals—never states—who commit heinous crimes, thereby promoting justice for victims and deterring future violations[1][6]. Its jurisdiction applies only to crimes committed after July 1, 2002, and generally within the territories of states that have ratified the Rome Statute or where the UN Security Council refers situations[2][7]. The ICC’s structure consists of four main organs: the **Presidency**, overseeing administration and external relations; the **Judicial Divisions**, made up of 18 judges handling pre-trial, trial, and appeals; the **Office of the Prosecutor**, responsible for investigations and prosecutions; and the **Registry**, managing judicial and administrative support[3][5][7]. The **Assembly of States Parties** governs the Court’s management, elects judges and prosecutors, and approves the budget[3][5]. Since 2018, the ICC has had jurisdiction over the crime of aggression, holding leaders accountable for illegal wars, a significant expansion of its mandate achieved through amendments to the Rome Statute[4]. The ICC currently conducts investigations and trials across multiple continents, addressing ongoing conflicts and atrocities[4][6]. Notably, the ICC also works through the **Trust Fund for Victims**, which provides reparations and assistance to victims and their families, emphasizing