Qatar's Role in the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
Introduction
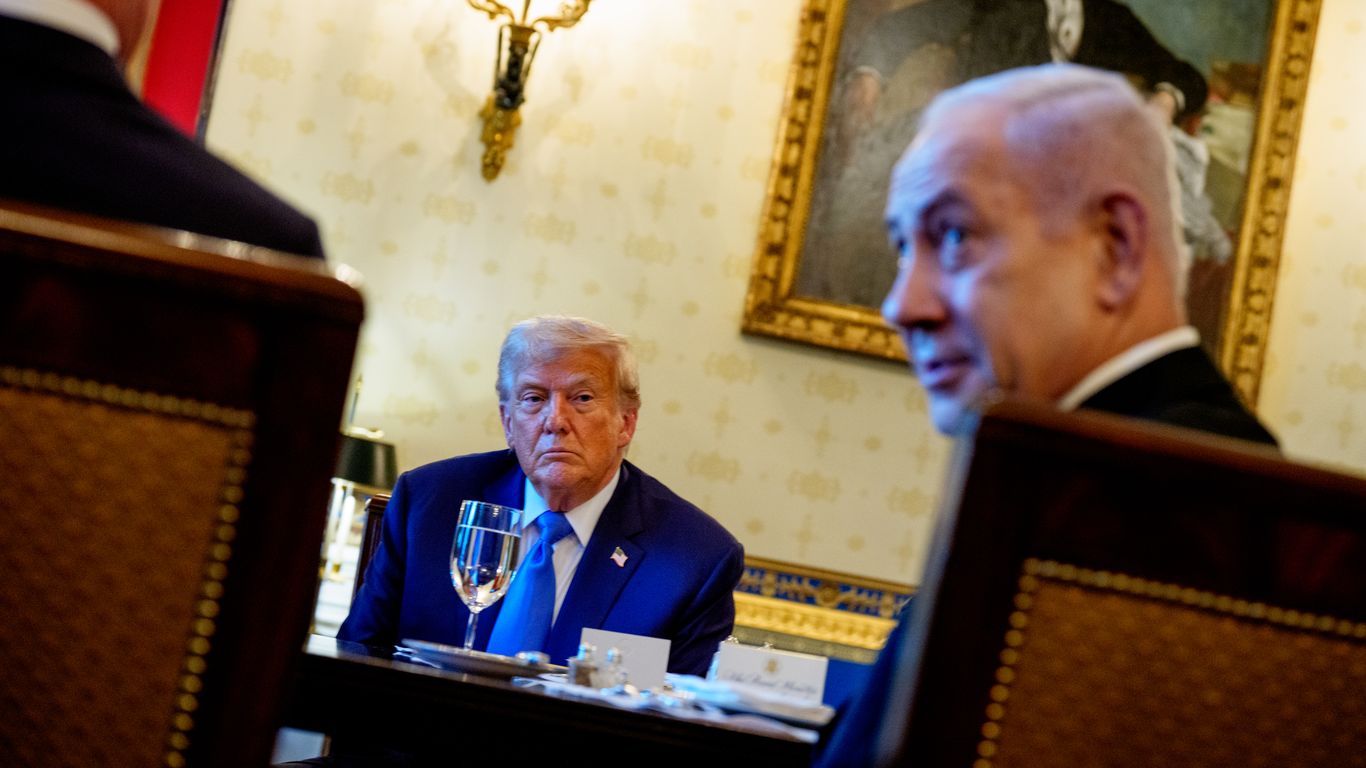
Qatar's prime minister, Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman Al Thani, has accused Israel of not caring about the hostages in the Gaza Strip. This was in response to Israel's recent attack on Hamas leaders in Doha. The prime minister, however, remained steadfast in his commitment to pushing for peace and stability in the region. In a speech to the U.N. Security Council, he vowed to continue this pursuit despite the ongoing conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
Qatar's Role in the Conflict
Qatar has been a key player in trying to broker a peace deal between Israel and the Palestinians. The country has hosted numerous talks and negotiations between the two sides, and its leaders have been vocal in their support for a two-state solution. However, their efforts have been met with resistance from Israel, who accuses Qatar of supporting and funding terrorist groups in the region.
The Need for International Support
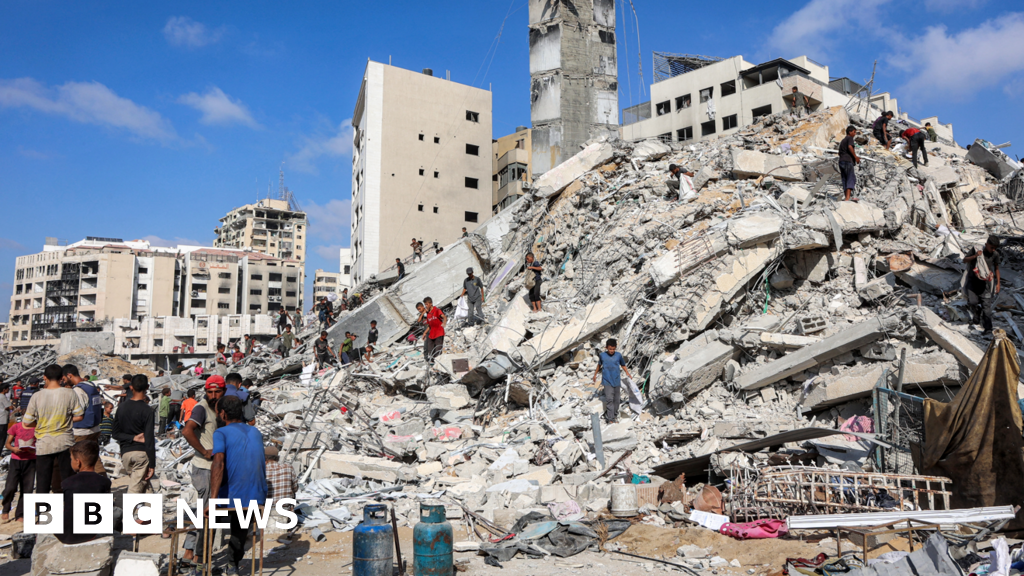
Qatar's prime minister emphasized the need for international support in resolving the conflict and ensuring the safety of the hostages in Gaza. He called on the U.N. to take action and hold Israel accountable for its actions. The ongoing conflict has resulted in numerous casualties and has created a humanitarian crisis in the region. It is crucial for the international community to step in and help bring an end to the violence and suffering of innocent civilians.
About the Organizations Mentioned
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is a pivotal international organization established in 1945, following the devastation of World War II, with the primary goal of maintaining global peace and security, fostering international cooperation, and promoting social progress. The UN Charter, signed by 51 founding member states, including the United States, the United Kingdom, China, and the Soviet Union, laid the foundation for this ambitious endeavor[1][3]. ## History and Structure The UN was born out of the failures of its predecessor, the League of Nations, which failed to prevent World War II. Key planning meetings, such as the Dumbarton Oaks Conference in 1944, defined the UN's structure, which includes the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat[1][6]. The Security Council, with five permanent members (the United States, China, France, Russia, and the United Kingdom), holds significant influence due to its veto power[2]. ## Key Achievements Over the years, the UN has played a crucial role in conflict resolution, human rights advocacy, and sustainable development. Notable achievements include the establishment of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948 and the implementation of numerous peacekeeping missions worldwide[3][4]. The UN has also been instrumental in addressing global challenges such as climate change and pandemics through its various programs and agencies. ## Current Status Today, the UN comprises 193 member states, with its most recent addition being South Sudan in 2011[5]. The organization continues to evolve, addressing emerging issues like digital governance and cybersecurity. Despite challenges, the UN remains a cornerstone of international diplomacy and cooperation. ## Notable Aspects The UN's work is not limited to politics; it also impacts business and technology through initiatives that promote sustainable development and digital inclusion. Its role in setting global standards and fostering international cooperation makes it a significant player in shaping the
🔗 Connected Events Overview
Discover related stories and their connections to this article
📊 Quick Insights
📅 Connected Events Timeline
Explore connected events with detailed insights and relationships
👥 People Involved in Connected Events
Connected through:
🏢 Organizations & Products
Key entities mentioned across connected events
🏢 Organizations
🛍️ Products
💡 Connected Events Insights
Discover patterns and trends across related stories
🔥 Trending Topics
Trending Blogs in Politics

Casey Means Faces Uphill Battle as Surgeon General Nominee in Vaccine Scrutiny
Casey Means, Trump's surgeon general pick, faces uphill confirmation amid vaccine questions and Kennedy health policy ties.
Mamdani's Bold White House Pitch to Trump
Zohran Mamdani meets President Trump at the White House to discuss a $21B housing plan for Sunnyside Yard and bipartisan housing reform.

Missing FBI Records Spark Epstein Files Controversy
CNN review finds dozens of FBI witness interviews missing from Epstein files, fueling questions about transparency.

White House Strategy: Israel Might Strike Iran First
Exploring White House push for Israel to strike Iran first, amid worries of retaliation, casualties, and political calculations.

Federal Crackdown on Medicaid Fraud: Minnesota First, Nationwide Expansion
Trump administration unveils an aggressive crackdown on healthcare fraud, freezing Minnesota funds and expanding Medicare/Medicaid integrity nationwide.