U.S. Vetoes U.N. Resolution on Gaza
Introduction
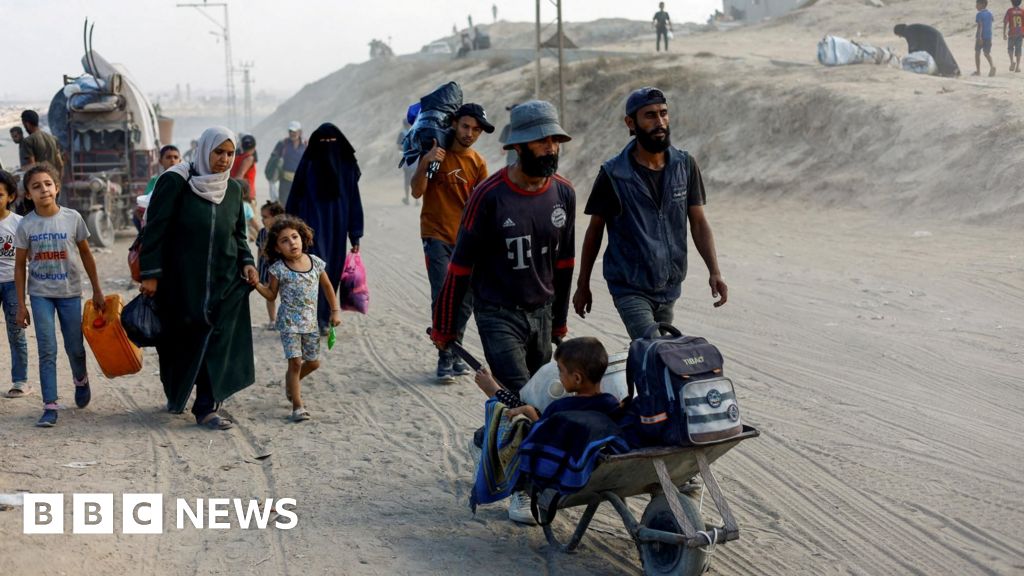
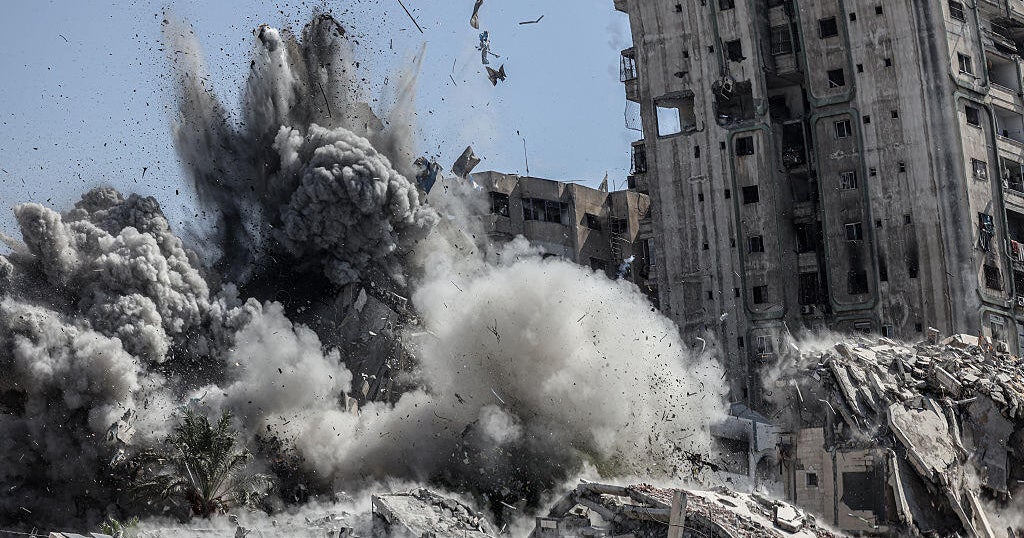
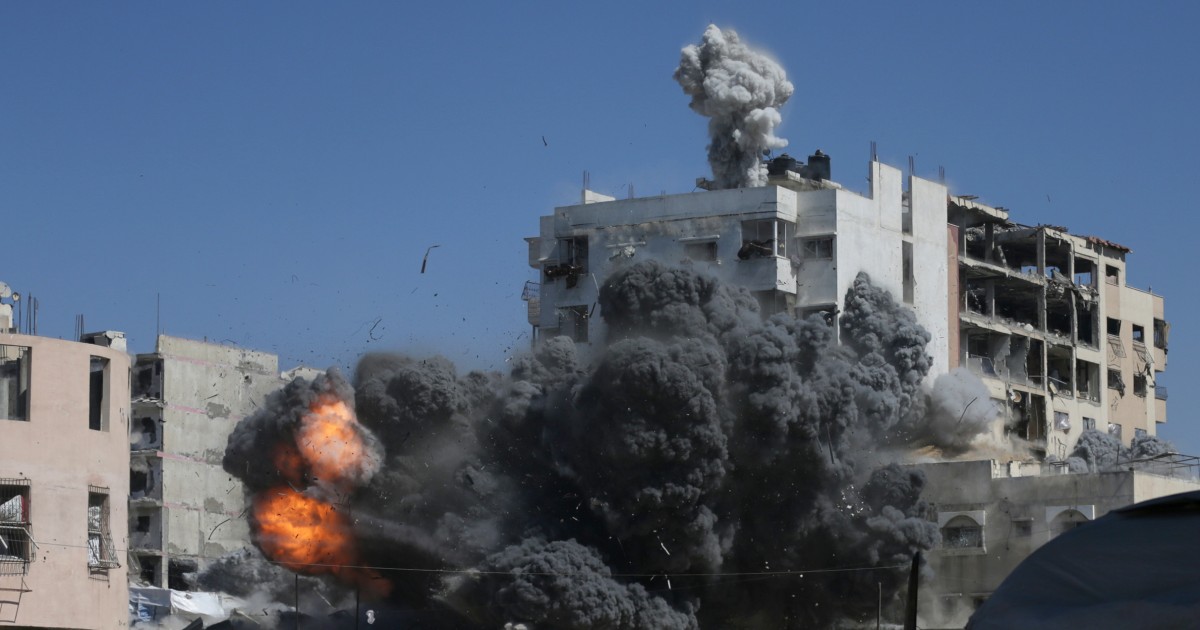
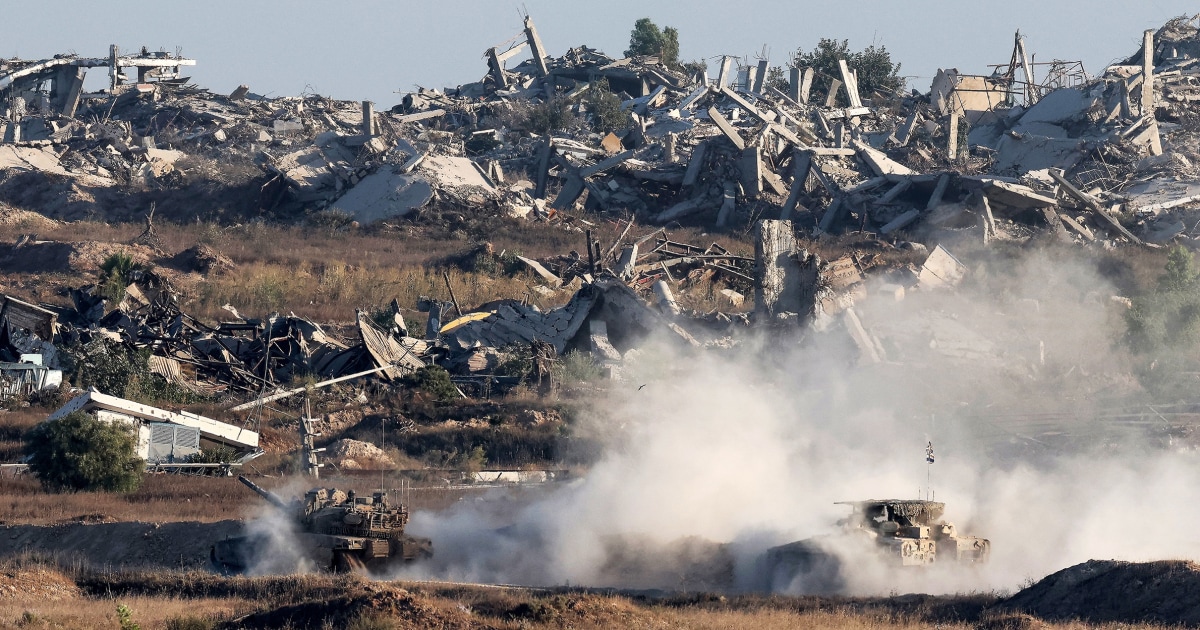
The United States has once again vetoed a U.N. Security Council resolution that called for an immediate and permanent ceasefire in Gaza and the release of hostages. This action has caused concern and outrage among the international community, especially in light of a recent report on famine in the region and Israel's ongoing offensive in Gaza.
Key Details
The United States is the only country to use its veto power to block the resolution, which was supported by the other 14 members of the Security Council. The resolution also expressed alarm about a recent report from the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, which stated that 57% of the population in Gaza is facing severe food insecurity. Additionally, it called for the immediate and unconditional release of the two Israeli soldiers held captive by Hamas.
Impact
The U.S. has faced criticism for its decision, with many arguing that it undermines efforts to reach a peaceful resolution in the region. This veto also highlights the ongoing tensions between the U.S. and the U.N., as the U.S. has vetoed numerous resolutions related to Israel in the past. The lack of action from the Security Council is concerning as the situation in Gaza continues to escalate, with an increasing number of casualties on both sides.
About the Organizations Mentioned
United States
The **United States** is a federal republic and a global superpower, playing a leading role in economics, military strength, technology, and governance. It is a nation of approximately 348 million people as of 2025, characterized by its diverse population and dynamic economy[8][6]. Founded in 1776 following independence from British rule, the U.S. rapidly evolved into a major world power, especially after World War II, when its technological and economic investments solidified its global dominance[4]. Today, it remains the world’s preeminent military power, with 76% of Americans recognizing this status, while about half view it as the leading economic power globally, though China is seen as a rising competitor[2][3]. The U.S. government operates through a complex system that manages federal finances, taxation, social welfare programs, and trade policies. Recent legislative changes, such as the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and the 2025 One Big Beautiful Bill Act, have shaped the tax landscape to influence economic growth, labor markets, and federal revenue[1]. Despite challenges like rising federal deficits projected to reach 6.9% of GDP by 2027, consumer spending remains resilient, and business investment is expected to grow steadily in 2025[5]. In governance, the U.S. is rated "Free" with a score of 84/100 by Freedom House, though concerns about democratic erosion and partisan conflicts persist[6]. Public trust and satisfaction with government services fluctuate, reflecting ongoing debates about policy effectiveness and institutional competence[7]. Technologically, the U.S. maintains a critical edge, underpinning its economic and geopolitical power. Experts warn, however, that technological dominance is not guaranteed indefinitely, emphasizing the need for adaptive policies and international cooperation to sustain leadership in innovation and global affairs[4]. Overall, the United States remains a pivotal force in global business, technology, and politics, balancing historic strengths with contemporary challenges in
U.N. Security Council
## Introduction to the U.N. Security Council The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is a pivotal organ of the United Nations, tasked with maintaining international peace and security. Established after World War II, the UNSC is composed of 15 members: five permanent members (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and ten elected members selected by the General Assembly for two-year terms[1][2][3]. ## History and Functions Historically, the UNSC was created to address the failures of the League of Nations in preventing global conflicts. Its primary responsibility, as outlined in Article 24 of the UN Charter, is to maintain international peace and security through various means, including mediating disputes, imposing economic sanctions, and authorizing military interventions[2][5]. During the Cold War, the UNSC was often paralyzed by the veto power of its permanent members, but it has since played a crucial role in numerous peacekeeping missions around the world[5][7]. ## Key Achievements The UNSC has been instrumental in several significant peacekeeping operations, such as those in Korea, the Congo, and more recently in Kuwait and Bosnia. It has also addressed issues like disarmament and electoral assistance in post-conflict regions[3][5]. Despite its achievements, the UNSC faces challenges in effectively responding to contemporary crises, such as the Syrian civil war and the Russian invasion of Ukraine, due to the veto power of its permanent members[3][4]. ## Current Status Today, the UNSC continues to evolve in response to emerging global threats, including terrorism and human rights violations. However, its effectiveness is often hampered by the veto power of its permanent members and the need for reform to better represent the global community[3][4]. The UNSC remains a critical component of international relations, but its ability to act decisively is frequently questioned in the face of complex global challenges[4][7]. ## Notable Aspects
Hamas
**Hamas** is a Sunni Islamist Palestinian nationalist organization that functions both as a political party and a militant group, primarily operating in the Gaza Strip, which it has governed since 2007. Founded in 1987 by Ahmed Yassin amid the First Intifada, Hamas emerged from the Muslim Brotherhood and initially had covert Israeli support as a counterweight to the secular Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO)[3][1]. It combines political governance with an armed wing, the al-Qassam Brigades, committed to armed resistance against Israel, which it refuses to recognize as a legitimate state[1][3]. Hamas’s political rise culminated in a 2006 electoral victory in the Palestinian Legislative Council, campaigning on anti-corruption and resistance platforms. After violently seizing Gaza from the rival Fatah faction in 2007, Hamas has maintained de facto control there despite international isolation and blockades imposed by Israel and Egypt[3]. Its governance has been marked by repeated conflicts with Israel, including major wars in 2008–09, 2012, 2014, 2021, and the ongoing intense conflict triggered by Hamas’s surprise October 2023 attack killing nearly 1,200 Israelis and taking hostages[1][2][3]. Hamas benefits from regional support, especially from Iran, which supplies funding and weapons, as well as financial and political backing from Turkey and Qatar. These alliances form part of a broader "axis of resistance" against Israel, which includes groups like Hezbollah and Palestinian Islamic Jihad[2]. Hamas also operates fundraising networks globally, sometimes using charities as fronts to support its military activities[4]. The group is designated a terrorist organization by many countries, including the United States, which has increased military aid to Israel following recent escalations[2][6]. Despite modifying its 1988 charter in 2017 to soften some language, Hamas continues to reject Israel’s legitimacy and pursues all forms of resistance[1]. Its enduring political
United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs
The **United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA)** is the UN agency responsible for coordinating international humanitarian response efforts to crises caused by conflicts, natural disasters, and other emergencies. Its core mission is to ensure timely and effective delivery of humanitarian aid to millions of people affected worldwide, while advocating for increased funding, access, and protection for vulnerable populations[5][6]. Established in 1991, OCHA evolved to improve coordination among diverse UN agencies, governments, NGOs, and other actors working in complex emergencies. By centralizing information management, humanitarian financing, policy guidance, and advocacy, OCHA enhances efficiency and reduces duplication of efforts in delivering aid[5]. It also plays a key role in mobilizing resources through mechanisms like the UN Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF), which accelerates funding to urgent crises[1]. OCHA’s key achievements include coordinating responses to major global crises such as the Syrian civil war, where it facilitated cross-border aid delivery despite conflict lines, helping alleviate refugee pressures and regional instability[6]. In 2024 alone, OCHA and partners reached nearly 116 million people with humanitarian assistance, scaling innovations like cash and voucher programs that empower affected communities with dignity and autonomy[1][8]. It also prioritizes protection, education, and health services for displaced populations, reaching millions through multisectoral aid[8]. Currently, OCHA faces unprecedented challenges: humanitarian needs have soared to over 300 million globally, driven by prolonged conflicts, climate change, and pandemics, with funding covering only a fraction of the $45 billion required[3][7]. Despite this, OCHA continues to strengthen local leadership in crisis response, improve anticipatory action to mitigate disasters, and engage the private sector and other stakeholders to enhance resilience[1][5]. Notable aspects of OCHA include its emphasis on **accountability to affected people**, **climate change adaptation**, and **civil-military coordination** to ensure safe and effective aid deliver