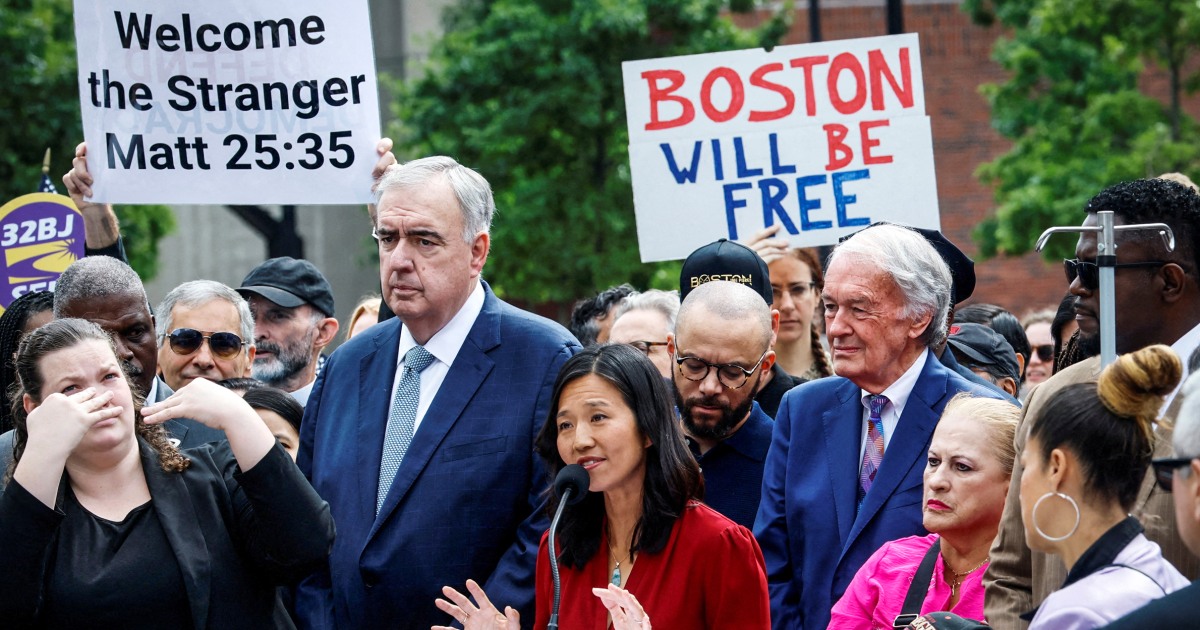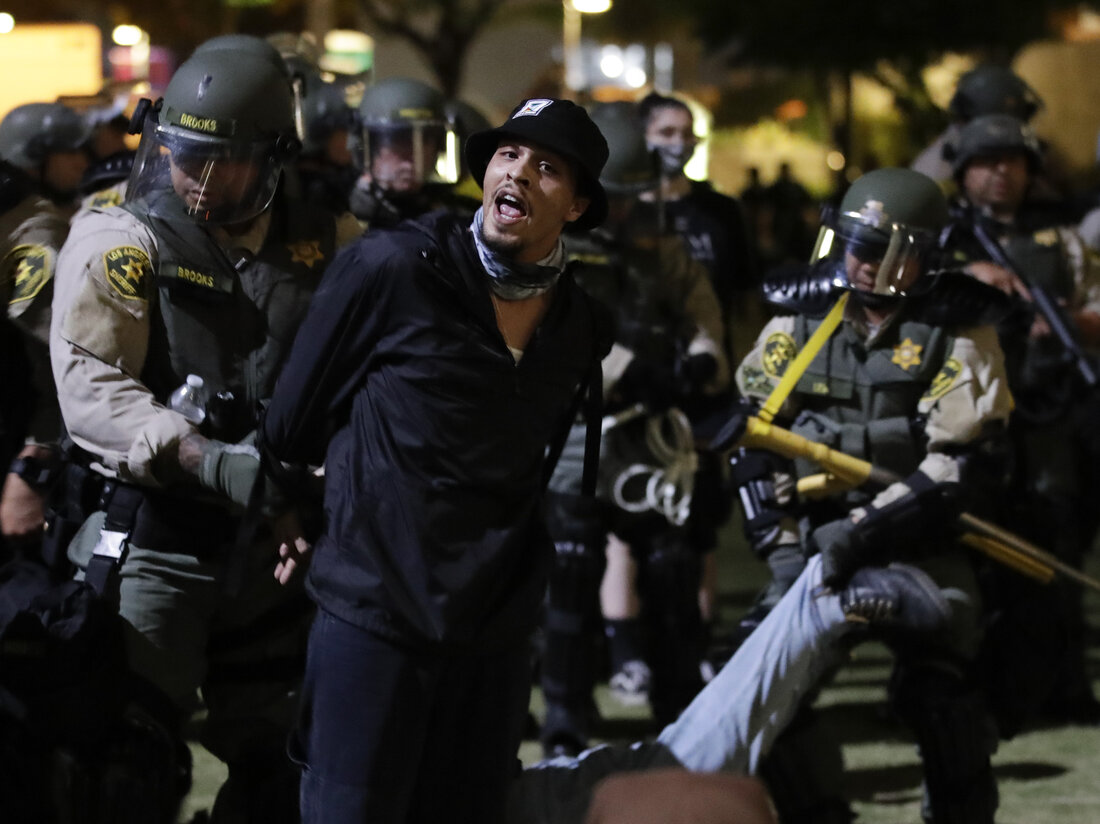ICE Raids Spark Controversy over Treatment of South Korean Workers

Introduction
On August 28, 2021, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) conducted a raid at a Hyundai electric vehicle site in Georgia, detaining multiple South Korean workers. This action has sparked an angry response from the South Korean government, who have called it an unjust infringement of people's rights. The raid has caused concern and uproar among both South Koreans and Americans, raising questions about immigration policies and the treatment of foreign workers in the United States.
Key Details
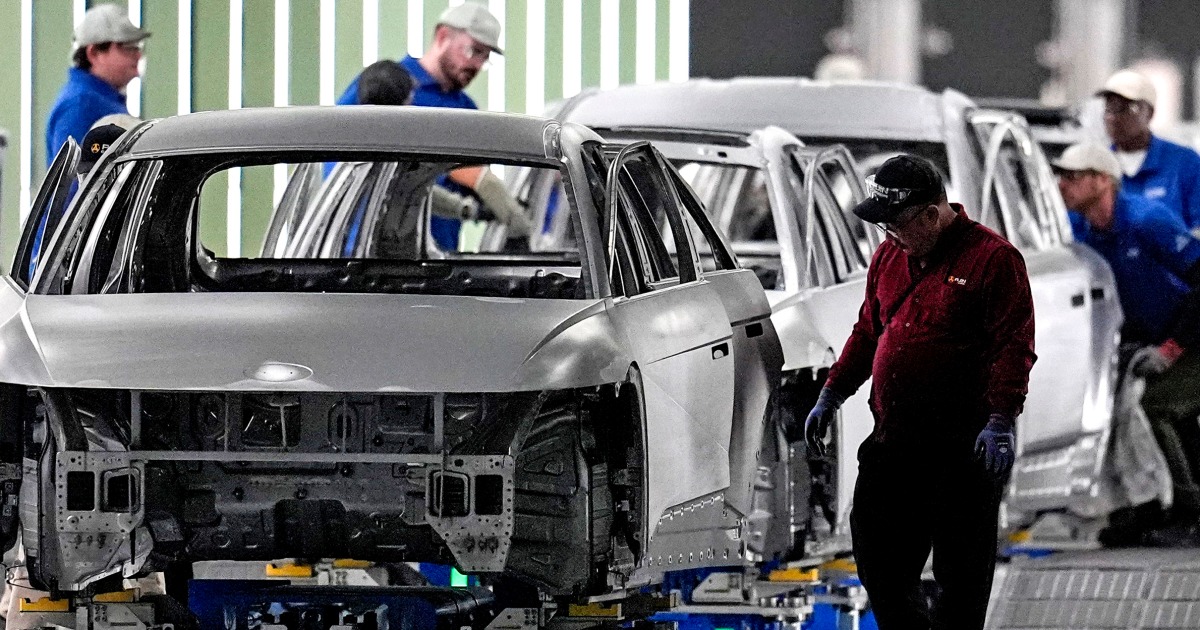
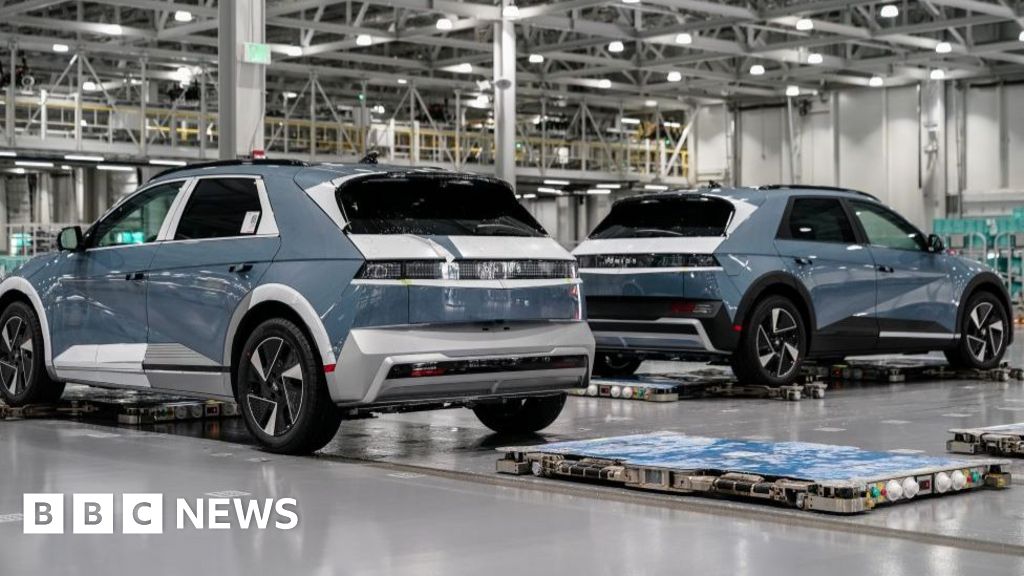
The detained South Korean workers were employed by a subcontractor for Hyundai Motor Manufacturing Alabama, and were in the US on business visas. ICE officials claim that the workers were in violation of their visa terms, but the South Korean government argues that they were not involved in any criminal activities and were in fact working legally. This incident has highlighted the complexities of US immigration policies and the potential mistreatment of foreign workers. It also brings attention to the impact of such raids on the affected workers, their families, and the companies they work for.
Impact
The detention of the South Korean workers has caused a rift between the two countries and has raised concerns about the treatment of non-American workers in the US. It also raises questions about the legalities and ethics of ICE raids and the impact they have on not only the individuals targeted, but also their families and communities. The incident has sparked a larger conversation
About the Organizations Mentioned
Immigration and Customs Enforcement
**Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE)** is a federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Established by the Homeland Security Act of 2002, ICE was created in response to the 9/11 attacks to enhance national security and protect public safety. The agency's primary mission is to enforce federal laws related to customs, trade, and immigration, focusing on cross-border crime and illegal immigration[1][2][3]. **History and Structure:** ICE was formed by merging the U.S. Customs Service and the Immigration and Naturalization Service. It operates with over 20,000 staff across more than 400 global offices, with an annual budget of approximately $8 billion[3]. The agency is structured into several key directorates, including **Enforcement and Removal Operations (ERO)**, which handles immigrant detention and deportation, and **Homeland Security Investigations (HSI)**, which investigates transnational crimes[1][2]. **Key Functions and Achievements:** ICE is known for its immigration enforcement efforts, particularly in interior regions of the U.S. It conducts investigations into human trafficking, terrorism, and other transnational crimes. Despite controversy over policies like family separation and detention conditions, ICE has made significant strides in combating illegal activities and protecting national security[4][6]. **Current Status and Notable Aspects:** Today, ICE continues to face challenges and controversy, particularly regarding its enforcement practices and impact on immigrant communities. The agency's actions can have profound effects on local economies and social services, as fear of ICE may deter undocumented immigrants from accessing essential services[6]. Despite these challenges, ICE remains a crucial component of U.S. immigration policy, working to balance enforcement with humanitarian concerns.
Hyundai Motor Manufacturing Alabama
## Overview Hyundai Motor Manufacturing Alabama (HMMA) is Hyundai Motor Company’s first and only U.S.-based automotive manufacturing plant, located in Montgomery, Alabama[1][4]. Established in 2005, HMMA is a cornerstone of Hyundai’s North American strategy, producing vehicles and engines specifically for the U.S., Canadian, and Puerto Rican markets[1][4]. The facility represents a major investment—over $1.7 billion—and has become a significant economic driver for Alabama, employing approximately 4,200 people and supporting thousands more through its supply chain[1][4]. ## What HMMA Does HMMA specializes in the final assembly of Hyundai vehicles and engines. Its production lines currently manufacture the Sonata and Elantra sedans, the Santa Fe SUV, and the Santa Cruz compact pickup truck[1]. The plant has an annual production capacity of about 400,000 vehicles and more than 700,000 engines, making it one of the largest automotive manufacturing facilities in the Southeastern United States[1]. HMMA’s operations are tightly integrated with Hyundai’s global quality and technology standards, ensuring that vehicles built in Alabama meet the same benchmarks as those produced in South Korea[5]. ## History and Key Achievements Hyundai selected Montgomery for its U.S. plant after extensive lobbying by Alabama officials, attracted by the state’s skilled workforce, strategic location, robust automotive supply chain, and business-friendly environment[1][3]. Groundbreaking took place in 2002, with the first Sonata rolling off the line in March 2005[1][3]. This marked Hyundai’s commitment to “Made in America” manufacturing and helped the brand strengthen its presence in the competitive North American market[3]. Since its inception, HMMA has been recognized for its economic impact, creating high-paying jobs and fostering regional growth[2][4]. The plant has also received accolades for its environmental and safety management practices, reflecting Hyundai’