Notre Dame Dares to Disrupt SEC Dominance in College Football

Notre Dame’s Bold Move in College Football
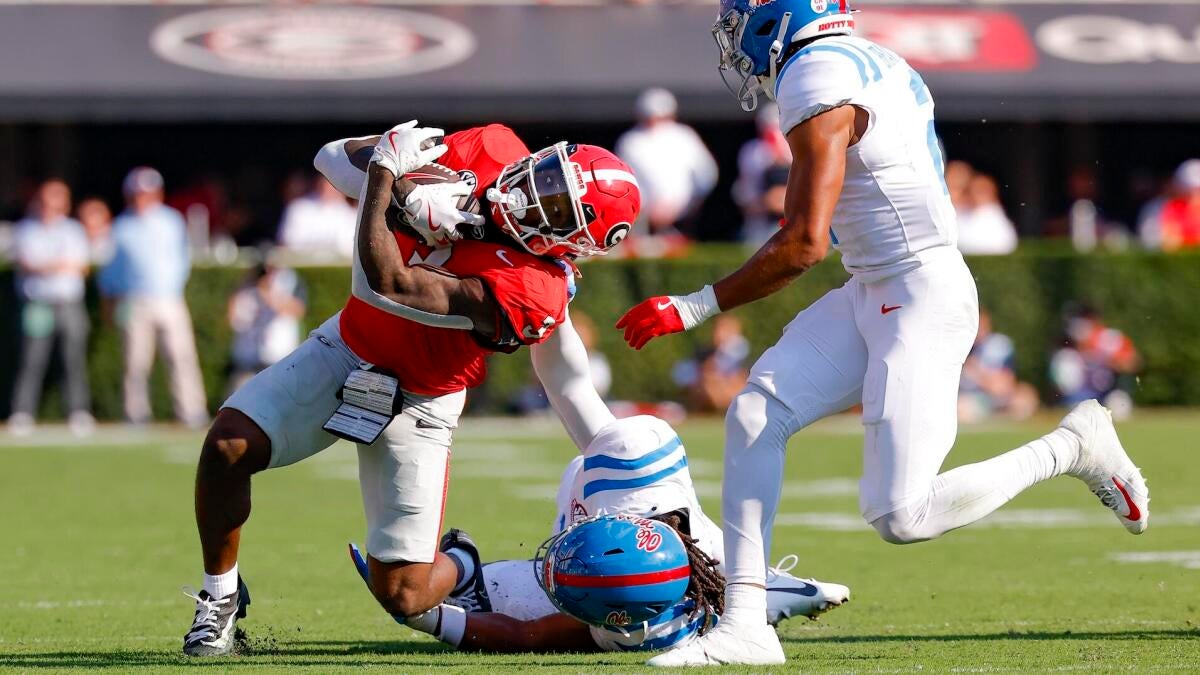
Notre Dame’s recent decision to withdraw from bowl game consideration signals a new era in college football rivalries. This move isn’t just about stepping back; it’s a strategic declaration that challenges the status quo, especially targeting the powerhouse SEC. By opting out, Notre Dame positions itself as a disruptor, refusing to follow traditional paths and demanding respect on its own terms.
Targeting the SEC’s Dominance
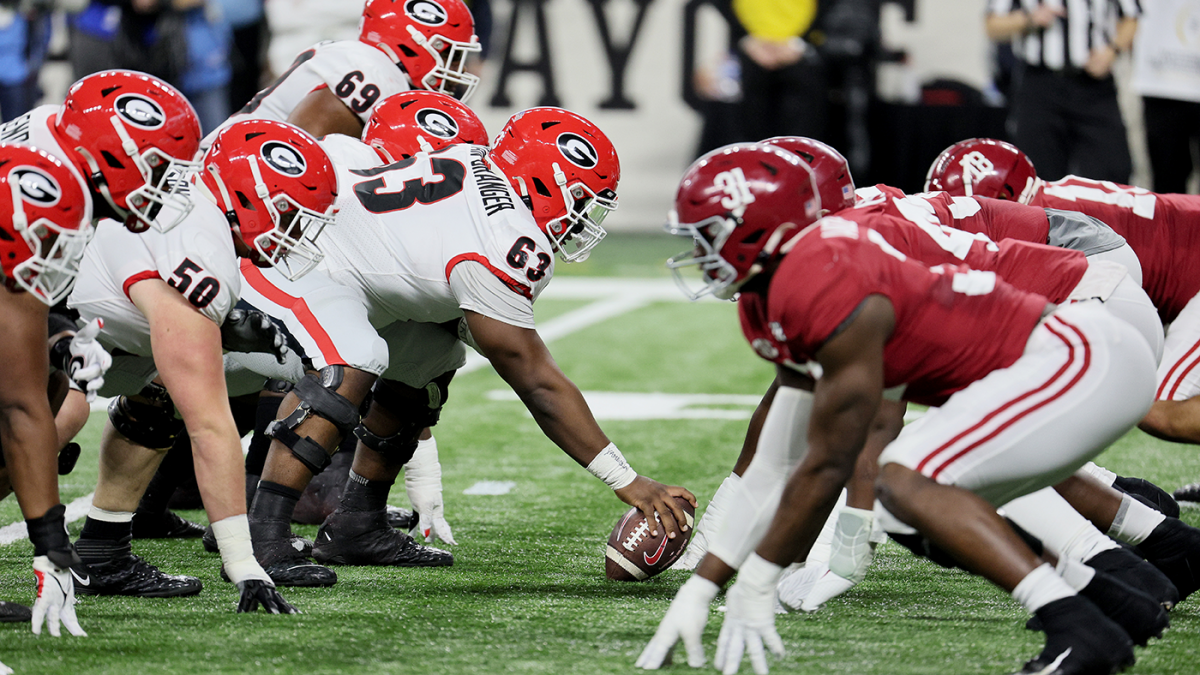
The SEC has long been viewed as the dominant force in college football, often shaping playoff selections and national narratives. Notre Dame’s stance directly confronts this dominance, suggesting that the Fighting Irish are willing to reshape competitive dynamics. This could shift recruiting battles, media coverage, and fan engagement, intensifying rivalries across conferences.
Implications for the Future
This declaration of “war” is more than rhetoric; it highlights growing tensions about fairness and influence in college football. Notre Dame’s move may inspire other programs to rethink their strategies and challenge established powers, potentially transforming how the sport evolves in the coming years.
About the Organizations Mentioned
Notre Dame
## Overview The University of Notre Dame (often referred to simply as “Notre Dame”) is a premier private Catholic research university located in Notre Dame, Indiana, USA. Founded in 1842 by Rev. Edward Sorin, C.S.C., it is renowned for its rigorous academics, storied athletics, and deep commitment to Catholic values. The university offers a comprehensive range of undergraduate, graduate, and professional programs, with its College of Engineering and other disciplines consistently ranked among the best nationally. ## Mission and Activities Notre Dame’s mission is to be “a powerful force for good,” educating students to be ethical leaders and global citizens who serve society through innovation, research, and community engagement[1]. The College of Engineering, for example, focuses on developing solutions to global challenges, educating the whole person, and conducting research that translates fundamental discoveries into impactful technologies[1]. The university also emphasizes global engagement, operating 12 global locations and offering 92 study abroad programs, which recently earned it the 2025 Senator Paul Simon Award for Comprehensive Internationalization[3]. ## History and Key Achievements Notre Dame’s history is marked by rapid expansion from a small college to a world-class research institution. Its football program, the Fighting Irish, is iconic in American collegiate athletics, competing as an independent in NCAA Division I FBS and playing at the historic Notre Dame Stadium[5]. Academically, Notre Dame is known for interdisciplinary research, particularly in areas like global affairs, engineering, and the humanities. The university’s leadership—including President Rev. Robert A. Dowd, C.S.C., and a robust administrative structure—guides its strategic direction[4]. ## Current Status and Notable Aspects Today, Notre Dame is recognized for its blend of tradition and innovation. It continues to invest in faculty, student support, and infrastructure, with recent strategic plans emphasizing inclusivity, sustainability, and the integration of faith and reason[1]. The university’s global footprint, commitment
SEC
The **Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)** is a U.S. federal regulatory agency established in 1934 to restore public confidence in the capital markets after the 1929 stock market crash. Its core mission is threefold: **protect investors, maintain fair, orderly, and efficient markets, and facilitate capital formation**[2][4][6]. The SEC enforces federal securities laws and regulates key market participants, including securities exchanges, brokers, dealers, investment advisors, and mutual funds. It requires companies offering securities to the public to disclose truthful and comprehensive information about their business and investment risks. It also oversees market intermediaries to prevent fraud, insider trading, and market manipulation[1][3][6]. Over time, the SEC’s role has evolved to address changing market dynamics and technological advances. It now provides investor education, facilitates capital formation especially for small businesses and fintech firms through initiatives like the Capital Raising Hub and FinHub, and actively engages in rulemaking with public input[1][6]. The SEC is led by five presidentially appointed commissioners and operates multiple divisions and offices, including a dedicated Division of Enforcement responsible for investigating violations, pursuing administrative actions, and litigating cases in federal courts[3]. It also supports whistleblowers who report fraudulent activities[1]. Notable achievements include developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks such as the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, pioneering investor protection laws, and adapting regulations to new challenges like digital asset markets. The SEC's enforcement actions and policy leadership have been crucial in maintaining market integrity and investor trust in U.S. financial markets[2][7]. Currently headquartered in Washington, D.C., the SEC continues to be a pivotal institution in U.S. financial regulation, balancing innovation with investor protection to uphold the stability and efficiency of the capital markets[5][6]. Its commitment to transparency, fairness, and accountability makes it a key player for business and technology news audiences interested in market oversight an