WHO Endorses GLP-1 Drugs for Obesity: Global Guidelines for Long-Term Care
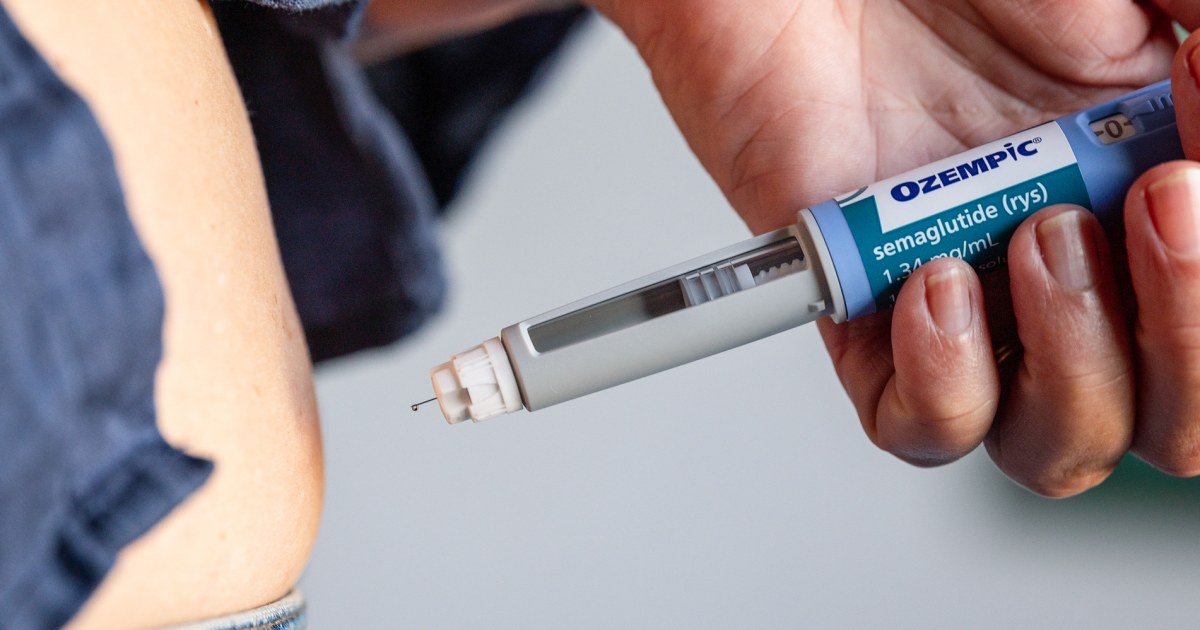
WHO Endorses GLP-1 Drugs for Obesity
The World Health Organization has officially recommended GLP-1 receptor agonists as a key tool for managing obesity in adults, signaling a major shift in global health policy. This marks the first time the U.N. agency has issued clinical guidance on pharmacological treatments for obesity, reflecting growing recognition of the disease’s complexity and chronic nature.
Guideline Highlights
The new guidelines stress that GLP-1 therapies—such as semaglutide, liraglutide, and tirzepatide—should be used long-term and combined with structured lifestyle interventions, including healthy eating, regular physical activity, and ongoing counseling. The WHO emphasizes that these medications are not standalone solutions but part of comprehensive, lifelong care programs.
Global Impact
With over a billion people affected by obesity worldwide, the WHO urges countries to improve access, prioritize those with the greatest medical need, and build equitable, sustainable treatment systems. The guidelines also call for a broader approach to obesity care, addressing not just weight loss but overall health and social determinants.
About the Organizations Mentioned
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations, established in 1948, with a mandate to promote global health, coordinate international responses to public health threats, and set standards for health policies and interventions[2]. Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, WHO operates in over 150 countries, working with governments, NGOs, and other partners to advance health equity, strengthen health systems, and respond to health emergencies. ## What WHO Does WHO’s core activities include monitoring global health trends, setting international health standards, providing technical assistance to countries, and serving as a forum for scientific and policy discussions on health issues[2]. The organization publishes influential reports such as the annual **World Health Statistics**, which tracks progress toward Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and provides a global “health report card”[1][8]. WHO also maintains the Model List of Essential Medicines, guiding countries on which drugs are most critical for public health[7]. In addition, WHO leads global campaigns on issues ranging from infectious disease eradication to noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), maternal and child health, and health emergencies[2][6]. ## History and Key Achievements WHO’s history is marked by landmark achievements, including the eradication of smallpox, near-eradication of polio, and the development of an Ebola vaccine[2]. The organization played a pivotal role in responding to the COVID-19 pandemic, coordinating global research, vaccine distribution, and public health guidance. In May 2025, WHO member states adopted the world’s first **Pandemic Agreement**, a historic step to improve international coordination and equity in future health crises[4]. WHO also spearheads initiatives like the Triple Billion Targets (healthier lives, universal health coverage, and protection from health emergencies) and technical policy packages targeting tobacco, alcohol, salt, and trans fat reduction[1][2]. ## Current Status and Notable Aspects WHO is currently implementing its **Fou