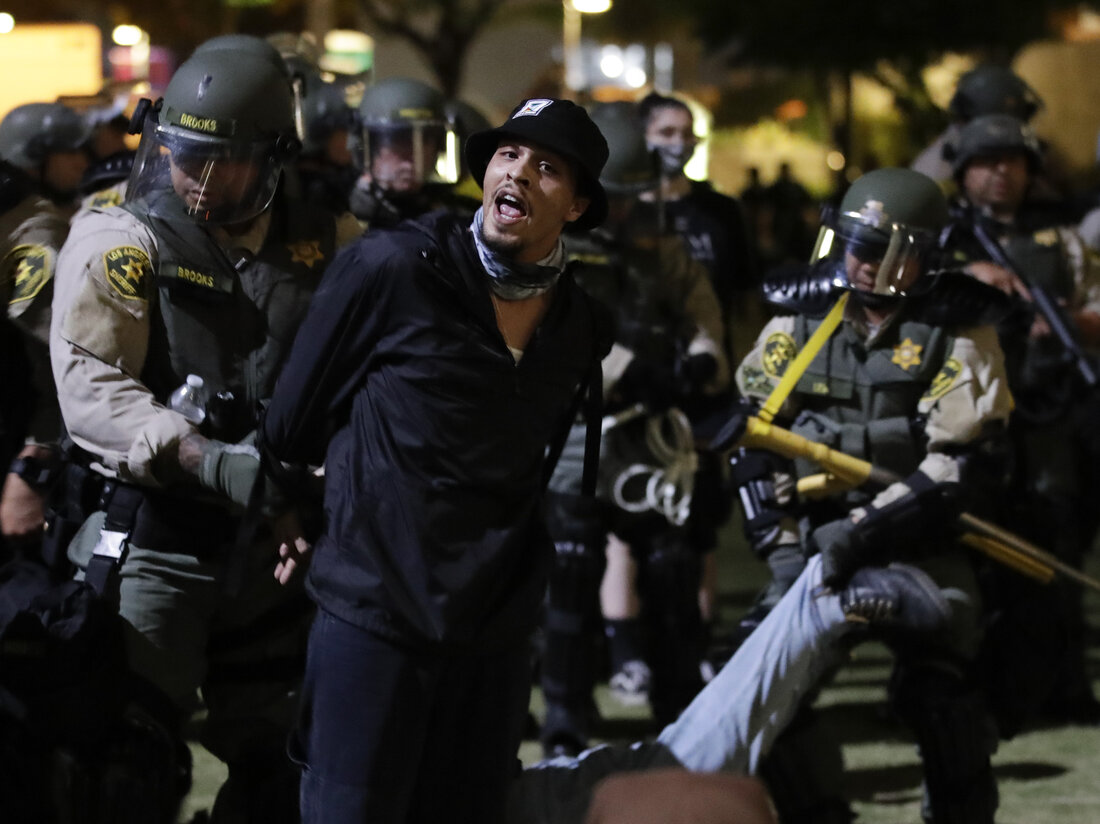California Takes Bold Step in Immigration Battle

Introduction
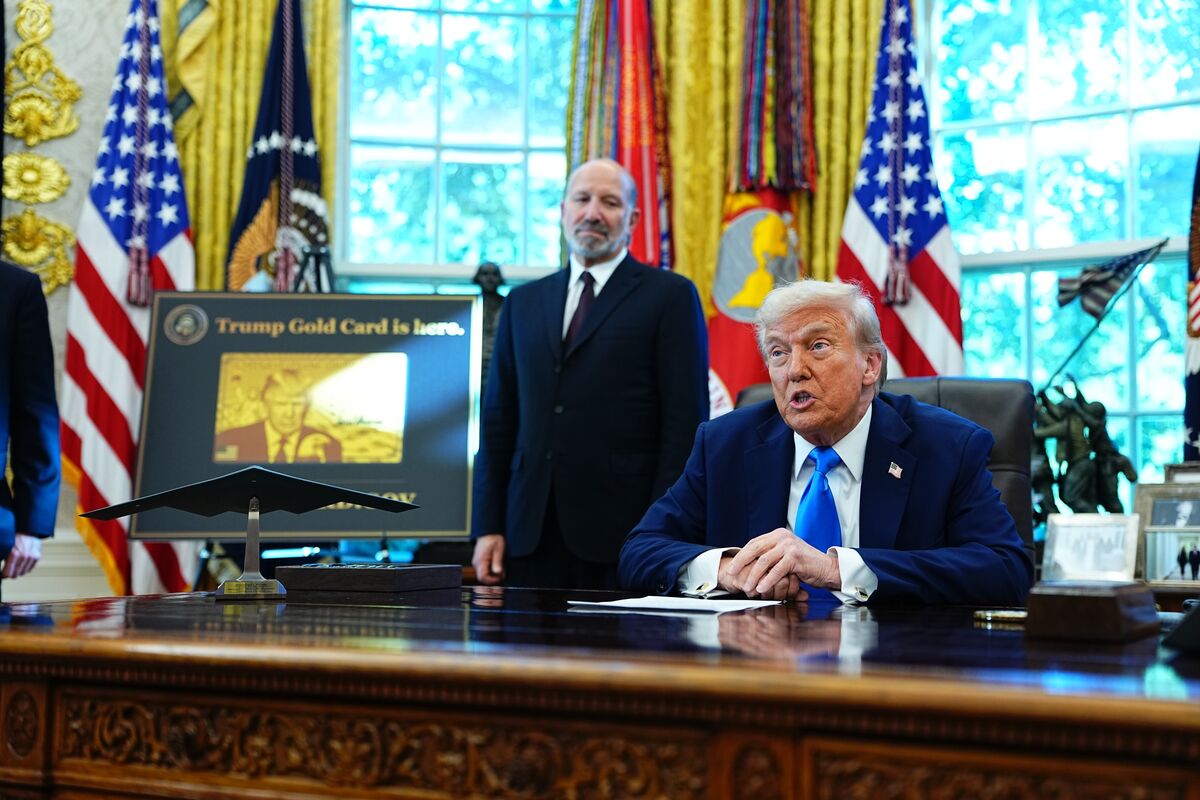
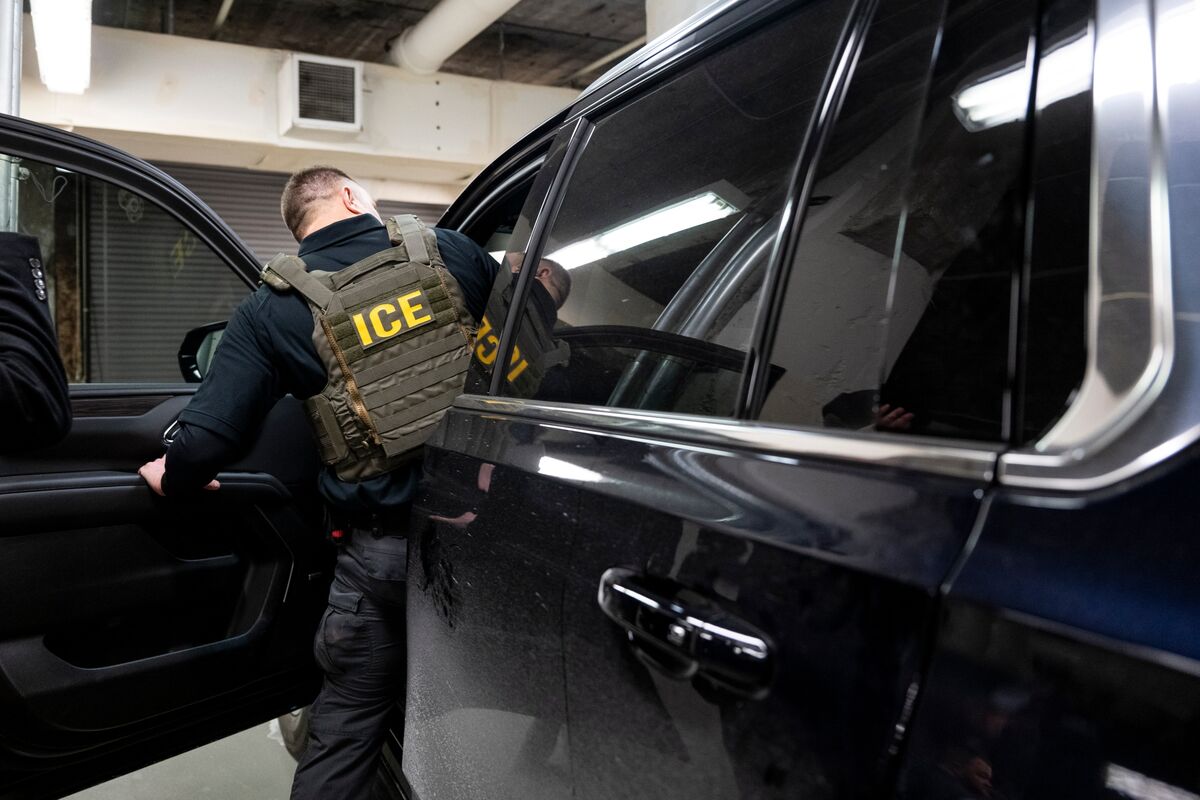
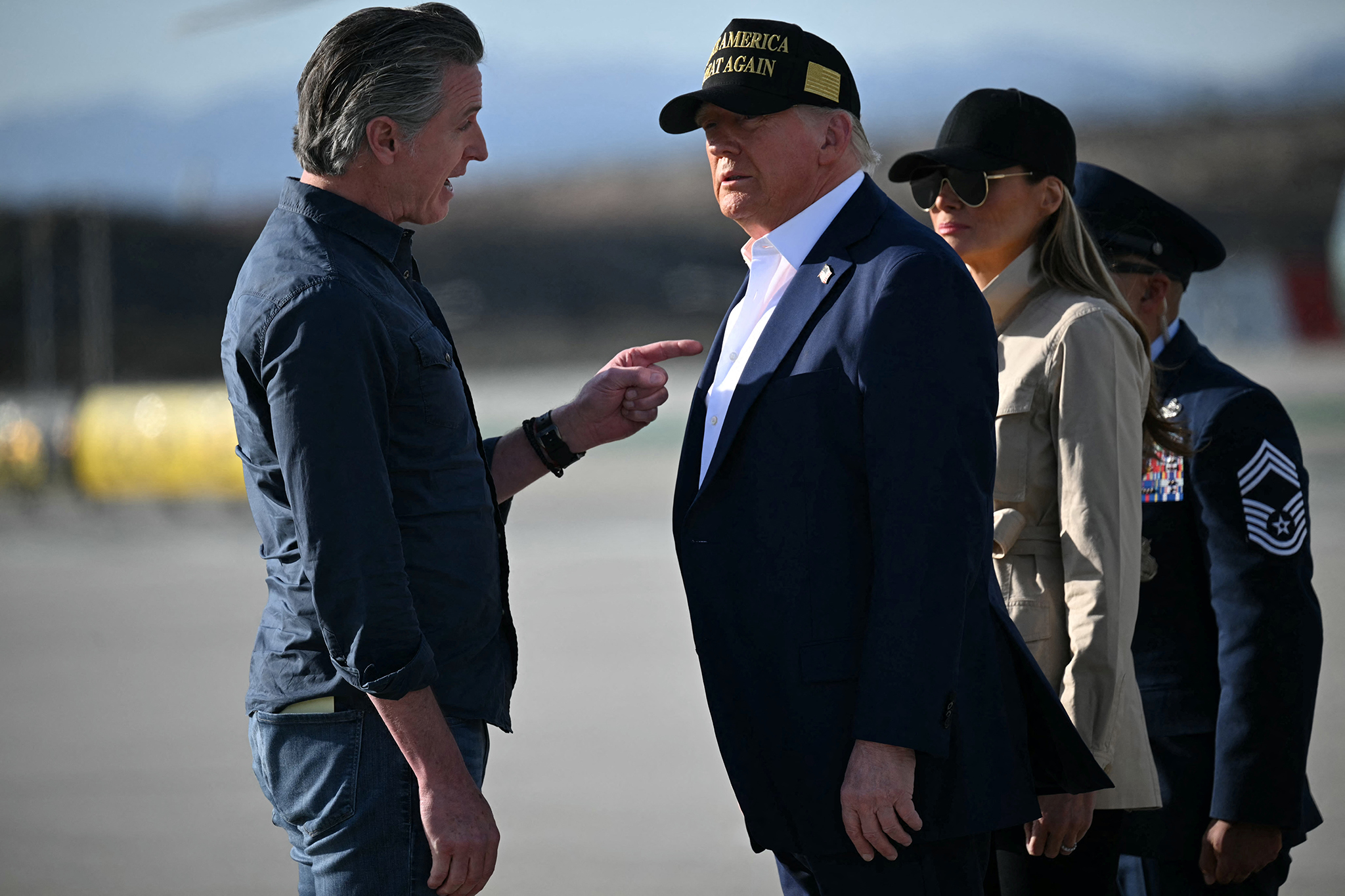
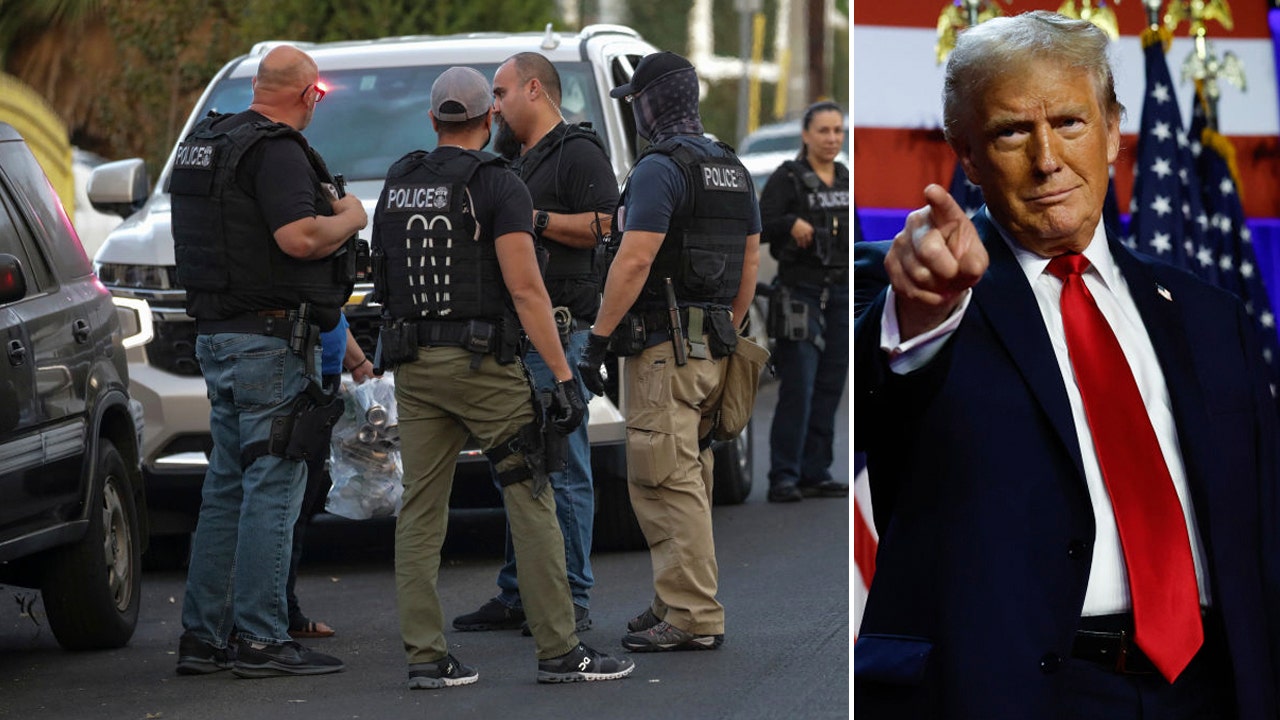
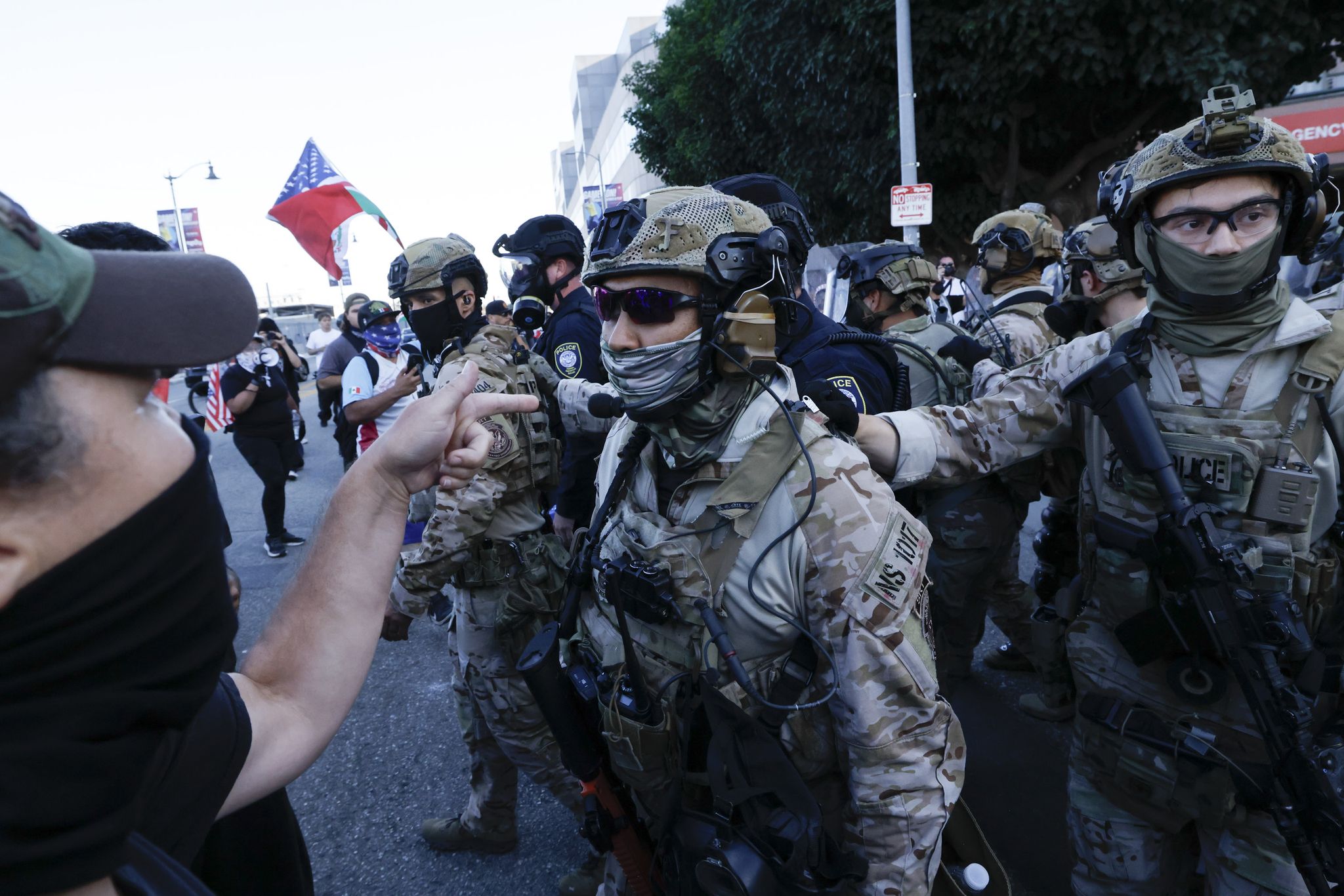
California has taken a bold step in the ongoing battle between the state and the federal government over immigration policies. Governor Gavin Newsom has signed a bill that prohibits Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) officers from wearing masks while carrying out their duties. This comes as a direct response to President Donald Trump's aggressive mass deportation efforts and his recent visit to the state, where he praised the work of ICE.
Key Details
The ban on masks not only serves as a direct challenge to the Trump administration's immigration policies, but it also highlights the state's commitment to protecting the rights of immigrants. The bill, which was introduced by Senator Ricardo Lara, aims to increase transparency and accountability in ICE operations by requiring officers to visibly display their name and agency on their uniforms. This move has been met with support from immigrant rights groups and advocates who have long criticized the secrecy surrounding ICE actions.
Impact
The ban on masks is a significant step in California's fight against Trump's aggressive immigration policies. It not only aims to protect the rights of immigrants, but it also holds ICE officers accountable for their actions. This move also sends a strong message to the federal government that California will not stand by and allow the rights of its residents to be violated. With this bill, California has once again asserted its position as a leader in progressive and inclusive policies, despite the continued resistance from the Trump
About the People Mentioned
Gavin Newsom
Gavin Christopher Newsom, born October 10, 1967, in San Francisco, California, is an American politician and businessman currently serving as the 40th governor of California since January 2019. Raised in an established San Francisco family and educated at Santa Clara University, where he studied political science, Newsom began his political career in 1996 with an appointment to the San Francisco Board of Supervisors, after serving briefly on the city’s Parking and Traffic Commission. Newsom was elected mayor of San Francisco in 2004, becoming the youngest mayor in over a century. His tenure was notable for progressive initiatives, including directing the city to issue marriage licenses to same-sex couples in 2004, a pioneering move in the national movement for marriage equality. He also launched the Healthy San Francisco program, expanding access to healthcare for uninsured residents. After serving as mayor until 2011, Newsom was elected lieutenant governor of California, holding that office from 2011 to 2019. As governor, Newsom has focused on progressive policy areas such as gun control, criminal justice reform, environmental protection, affordable housing, and universal healthcare access. His administration has prioritized tackling homelessness, improving public safety, and expanding educational opportunities. Notably, he imposed an early moratorium on executions in California and led the state's response to the COVID-19 pandemic, implementing some of the strictest health measures in the country. Newsom survived a recall election in 2021 and was re-elected in 2022, maintaining significant political influence in California. Newsom is also known for his entrepreneurial background, founding the PlumpJack Group, which grew into a substantial hospitality and wine business. He is married to Jennifer Siebel Newsom, and they have four children. Diagnosed with dyslexia in childhood, Newsom has spoken publicly about overcoming learning challenges while pursuing a career in public service[1][2][3][5][6][7].
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump, born June 14, 1946, in Queens, New York, is an American businessman, media personality, and politician. He graduated from the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School in 1968 with a degree in economics. In 1971, he took over his family’s real estate business, renaming it the Trump Organization, through which he expanded into building and managing skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. Trump gained widespread fame as the host of the reality TV show *The Apprentice* from 2004 to 2015, which helped establish his public persona as a successful entrepreneur. Trump entered politics as a Republican and was elected the 45th president of the United States, serving from 2017 to 2021. His presidency was marked by significant policy actions including tax cuts, deregulation, the appointment of three Supreme Court justices, renegotiation of trade agreements (notably replacing NAFTA with the USMCA), and a focus on immigration control including border wall expansion. He withdrew the U.S. from international agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the Iran nuclear deal, and engaged in a trade war with China. His administration’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic was criticized for downplaying the virus’s severity. Trump was impeached twice by the House of Representatives—first in 2019 for abuse of power and obstruction, and again in 2021 for incitement of insurrection—but was acquitted by the Senate both times. After losing the 2020 election to Joe Biden, Trump challenged the results, culminating in the January 6, 2021, Capitol riot. He remains a central figure in American politics, having won the 2024 presidential election and returned as the 47th president in 2025, continuing to promote policies aimed at economic growth, border security, and military strength[1][2][3][4].
About the Organizations Mentioned
Immigration and Customs Enforcement
**Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE)** is a federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Established by the Homeland Security Act of 2002, ICE was created in response to the 9/11 attacks to enhance national security and protect public safety. The agency's primary mission is to enforce federal laws related to customs, trade, and immigration, focusing on cross-border crime and illegal immigration[1][2][3]. **History and Structure:** ICE was formed by merging the U.S. Customs Service and the Immigration and Naturalization Service. It operates with over 20,000 staff across more than 400 global offices, with an annual budget of approximately $8 billion[3]. The agency is structured into several key directorates, including **Enforcement and Removal Operations (ERO)**, which handles immigrant detention and deportation, and **Homeland Security Investigations (HSI)**, which investigates transnational crimes[1][2]. **Key Functions and Achievements:** ICE is known for its immigration enforcement efforts, particularly in interior regions of the U.S. It conducts investigations into human trafficking, terrorism, and other transnational crimes. Despite controversy over policies like family separation and detention conditions, ICE has made significant strides in combating illegal activities and protecting national security[4][6]. **Current Status and Notable Aspects:** Today, ICE continues to face challenges and controversy, particularly regarding its enforcement practices and impact on immigrant communities. The agency's actions can have profound effects on local economies and social services, as fear of ICE may deter undocumented immigrants from accessing essential services[6]. Despite these challenges, ICE remains a crucial component of U.S. immigration policy, working to balance enforcement with humanitarian concerns.