Nasdaq Reaches Record High with Nvidia Leading Tech Rally

S&P 500 Reaches New High with Nvidia Leading Big Tech Rally
The Nasdaq Composite closed at a record high on Wednesday, driven by a surge in Nvidia shares. This marked the third time this month that the Nasdaq has reached a record high. The S&P 500 also saw gains, reaching its own record high. The rise in tech stocks, led by Nvidia, can be attributed to strong earnings reports and a positive outlook for the industry. With the tech sector playing a significant role in the overall market, this upward trend is a positive sign for investors. As the economy continues to recover, experts predict that the tech sector will play a crucial role in driving growth and stability in the market.
About the Organizations Mentioned
Nasdaq
**Nasdaq** (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is a premier American stock exchange, recognized as the second-largest globally by market capitalization and the first fully electronic stock market. Founded in 1971 and headquartered in New York City, Nasdaq revolutionized trading by introducing an automated, transparent, and efficient platform, setting a technological benchmark for global financial markets[1]. Nasdaq operates as both a stock exchange and a technology company through its parent, Nasdaq, Inc., which also owns multiple other U.S. and Nordic exchanges. It hosts over 4,000 listed companies, including prominent technology giants, foreign firms primarily from China and Israel, and a broad range of industries. Its indices, notably the Nasdaq Composite and Nasdaq-100, are key barometers of technology sector performance and innovation trends[1]. Historically, Nasdaq's achievements include pioneering electronic trading systems, leading market innovations such as the Advanced Computerized Execution System (ACES), and continuously enhancing market accessibility and liquidity. Its fully electronic model has driven high trading volumes, making it the most active U.S. stock market by volume. Nasdaq also plans to expand trading hours to 24 hours a day, five days a week, pending regulatory approval as of early 2025[1]. In recent years, Nasdaq has demonstrated robust financial growth; Q1 2025 earnings showed a 12.5% revenue increase year-over-year to $1.2 billion, with its solutions business growing 11%, reflecting strong demand for market technology and data services. The annual recurring revenue reached $2.8 billion, indicating solid future revenue visibility[2]. Nasdaq continues to benefit from megatrends such as artificial intelligence commercialization, semiconductor industry leadership, and cloud infrastructure expansion, which dominate the growth narrative on its platform[5]. Overall, Nasdaq remains a cutting-edge financial market hub that blends technology innovation with capital market leadership, serving as a vital engine for global busines
S&P 500
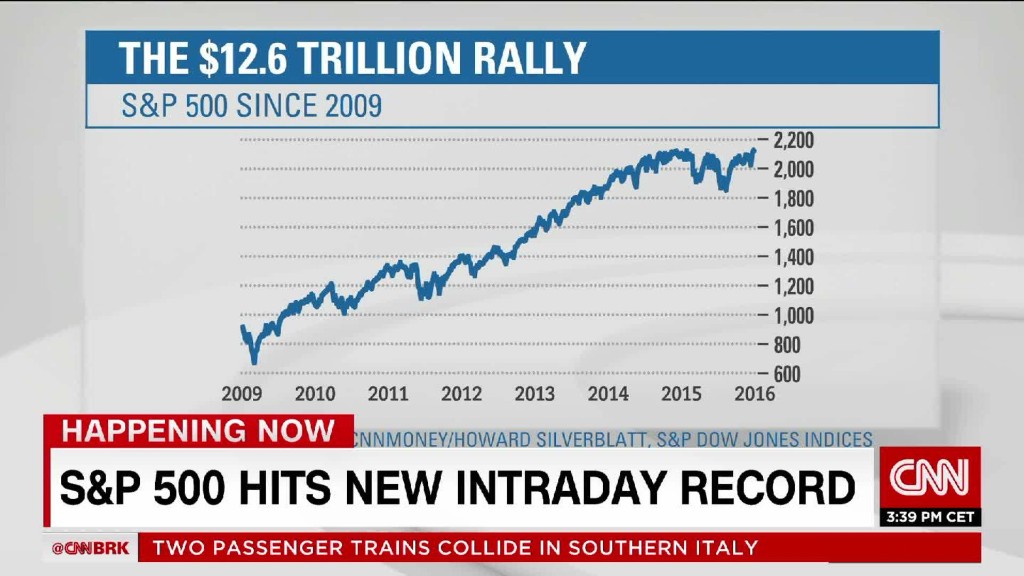
The S&P 500, officially known as the Standard & Poor’s 500, is a revered stock market index tracking the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States[1]. Managed by S&P Dow Jones Indices—a joint venture majority-owned by S&P Global—the S&P 500 is widely recognized as a leading barometer of the U.S. stock market and, by extension, the broader economy[1][7]. It accounts for roughly 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate value exceeding $57 trillion as of August 2025[1]. The index is weighted by market capitalization, meaning larger companies exert a greater influence on its movements[1][2]. Its top holdings include tech giants like Nvidia, Microsoft, Apple, and Alphabet, which together represent a significant portion of the index’s total value[1]. ## History and Evolution The S&P 500 traces its origins to 1923, when the Standard Statistics Company (later becoming Standard & Poor’s) launched an index of 233 companies[3]. In 1957, it expanded to include approximately 500 companies, formalizing the structure familiar today[3]. Over the decades, the index has evolved into a cornerstone of global finance, reflecting the dynamism of the U.S. economy and the rise of sectors like technology, healthcare, and consumer goods. ## Purpose and Impact The S&P 500 serves multiple critical roles: it is a benchmark for investment portfolios, a basis for passive index funds and ETFs, and a key input for economic forecasting tools like the Conference Board Leading Economic Index[1][6]. For companies, inclusion in the S&P 500 is prestigious and financially impactful, often triggering significant buying activity as funds tracking the index adjust their holdings[2]. For investors, the index offers a convenient, diversified exposure to the U.S. equity market through index funds and ETFs[4
Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation, founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem and headquartered in Santa Clara, California, is a pioneering American technology company best known for inventing the graphics processing unit (GPU) in 1999[1][2][4]. Initially focused on GPUs for video gaming, Nvidia has expanded its scope to serve diverse markets, including artificial intelligence (AI), high-performance computing (HPC), professional visualization, automotive technology, and mobile devices[1][3]. Nvidia’s GPUs, such as the GeForce series for gamers and the RTX series for professional applications, are central to its dominance, controlling over 90% of the discrete GPU market as of early 2025[1][4]. The company’s investment in CUDA, a parallel computing platform and API launched in the early 2000s, revolutionized GPU computing by enabling GPUs to accelerate a wide range of compute-intensive tasks, particularly in AI and scientific research[1][4]. By 2025, Nvidia commanded over 80% of the GPU market for AI training and inference and supplied chips to more than 75% of the world’s top 500 supercomputers[1]. Nvidia’s influence extends beyond hardware. It offers a comprehensive ecosystem including software platforms like Omniverse for 3D simulation and digital twins, AI frameworks such as MONAI for medical imaging, and Jetson for robotics and edge AI[2][3]. Its technologies power autonomous vehicle data centers, AI factories, and cloud gaming services like GeForce Now[2][7]. Financially, Nvidia achieved record full-year revenue of $130.5 billion in fiscal 2025, with a workforce of over 36,000 employees worldwide and a robust patent portfolio exceeding 8,700 applications[2]. The company is recognized for innovation and workplace excellence, topping Forbes’ "America’s Best Companies 2025" and Fast Company’s "World’s Most Innovative Companies"