Controversy Over Polygraph Tests in Government

Introduction
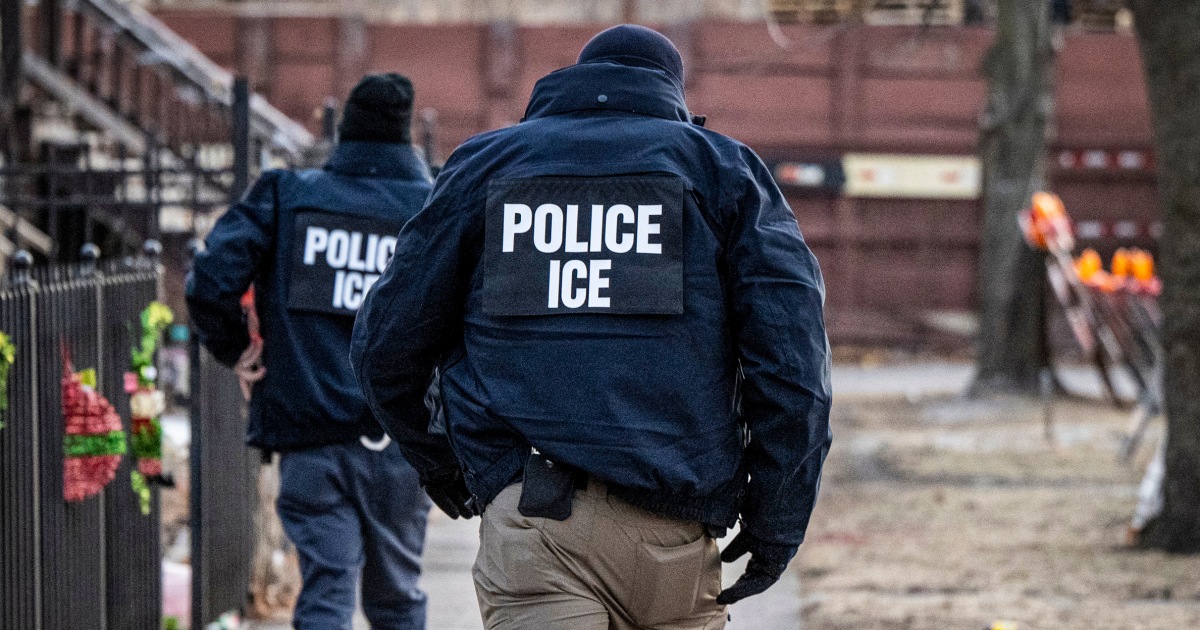
The Washington Post recently reported that the team of Fox News host, Pete Hegseth, was instructed to stop polygraph tests after a complaint was made to the White House. This comes amidst efforts by the defense secretary to put an end to damaging leaks to the media from Pentagon officials. The use of polygraph tests, also known as lie detector tests, has been a controversial topic in the government and has raised concerns about privacy and reliability.
Key Details
The incident was brought to light after a complaint was made to the White House regarding the use of polygraph tests on Pentagon officials. This move was seen as an attempt to prevent damaging leaks to the media, which have been a source of frustration for the defense secretary. However, this decision was met with criticism as polygraph tests have been known to produce unreliable results and can potentially infringe on an individual's privacy. In addition, it raises questions about the effectiveness of using such measures to prevent leaks.
Impact
With the use of polygraph tests being called into question, it is important for government officials to consider alternative measures to prevent leaks. This incident also highlights the need for a balance between protecting classified information and respecting the privacy of individuals. Moreover, this raises concerns about the use of polygraph tests in other government agencies and whether they are truly effective in preventing leaks. It
About the People Mentioned
Pete Hegseth
Pete Hegseth is an American government official, author, and former television personality. Born on June 6, 1980, he graduated from Princeton University in 2003 and later earned a master's degree in Public Policy from Harvard University's John F. Kennedy School of Government in 2013[1][4]. Hegseth was commissioned as an infantry officer in the Minnesota Army National Guard, serving in Guantanamo Bay, Iraq, and Afghanistan. He received several military awards, including two Bronze Star Medals and the Combat Infantryman Badge[3][4]. After his military service, Hegseth worked with organizations such as Vets for Freedom and Concerned Veterans for America, where he served as executive director and CEO, respectively[1][7]. He became a contributor to Fox News in 2014 and later co-hosted *Fox & Friends Weekend* from 2017 to 2024[1][5]. Hegseth has written several books, including *American Crusade* and *The War on Warriors*, the latter being a New York Times bestseller[3][5]. In November 2024, Hegseth was nominated by President-elect Donald Trump to be the Secretary of Defense. He faced a contentious confirmation process, with allegations of misconduct and financial issues. Despite these challenges, Hegseth was confirmed by the Senate on January 25, 2025, with Vice President JD Vance casting a tie-breaking vote[1][2]. As Secretary of Defense, Hegseth has been involved in several significant events, including ordering budget cuts and firing top military officers to "focus our military on its core mission"[2]. He has also been at the center of controversy regarding the use of the Signal messaging app for sharing sensitive information[2]. In September 2025, Hegseth addressed senior military leaders, emphasizing the need for tighter fitness standards and opposition to certain policies he termed "woke garbage"[1].
About the Organizations Mentioned
Fox News
## Overview Fox News, formally known as the Fox News Channel (FNC), is a leading American cable and satellite news network, renowned for its conservative-leaning commentary and round-the-clock news coverage. Launched in 1996 under the vision of Rupert Murdoch and Roger Ailes, it quickly established itself as a major force in U.S. media, challenging established networks with a distinctive blend of news reporting and opinion programming[2]. Today, Fox News is a flagship asset of Fox Corporation, a multinational mass media company controlled by the Murdoch family[1][6]. ## What Fox News Does Fox News delivers 24-hour news coverage, combining live reporting with opinion-driven shows that emphasize conservative perspectives[2][3]. Its programming spans breaking news, political analysis, business updates, and lifestyle content, reaching audiences via television, digital platforms, audio, and streaming services such as Fox Nation[3][7]. Fox News Media also operates Fox Business Network, Fox News Digital, Fox News Audio, and Fox Weather, collectively reaching nearly 200 million people monthly[3][7]. ## History and Growth Fox News launched on October 7, 1996, with innovative visual storytelling and a focus on personality-driven shows, setting it apart from competitors[2]. Despite initial challenges gaining carriage in major markets, it rapidly grew its audience by catering to viewers seeking an alternative to mainstream, left-leaning news outlets[2]. Over the years, it has expanded its digital footprint, launching streaming platforms and dominating social media metrics—most recently logging 1.1 billion YouTube views in a single quarter, more than any other U.S. news brand[7]. ## Key Achievements Fox News has been the most-watched cable news channel for over 23 consecutive years, routinely outperforming not only CNN and MSNBC but also broadcast networks like ABC, NBC, and CBS in primetime ratings[6][8]. Its top programs—*Fox & Friends*, *The Five
White House
The **White House Office** is a central organizational component within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP), tasked with supporting the President in managing day-to-day operations, policy formulation, and political affairs. It is headed by the White House Chief of Staff and staffed by senior aides who report directly to the President, including those with titles such as Assistant to the President and Deputy Assistant to the President. These staff members are mostly political appointees without the need for Senate confirmation, allowing the President considerable discretion in shaping the office to suit each administration's priorities[1]. Historically, the White House Office was established in 1939 through Reorganization Plan 1 and Executive Order 8248 to provide immediate assistance to the President. It functions as the nerve center for presidential staff, physically located primarily in the West Wing, and plays a pivotal role in managing the President’s policy agenda, communications, and political strategy. Its flexible organization allows each President to tailor the staff composition and roles according to their governance style and objectives[1]. In the current context of 2025, the White House Office operates under the administration of President Donald J. Trump, who returned to office after the 2024 election. His administration emphasizes rejecting prior policies deemed extremist and focuses on enhancing quality of life, economic growth, and American energy dominance. The administration includes Vice President JD Vance and First Lady Melania Trump, among others, with a Cabinet advising on various governmental functions[4][6]. Recent initiatives linked to the White House’s operational sphere include the establishment of a new **Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE)** aimed at modernizing federal technology and software to boost government productivity. The DOGE agenda is implemented through the renamed United States DOGE Service within the Executive Office, reflecting a concerted push to leverage technology for administrative modernization[5]. Notably, the White House Office also coordinates national security and homeland security functions through the National Security Council staff, underscoring its central role
Pentagon
The **Pentagon** is the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense (DoD), serving as the central command center for the nation's military operations and strategic defense planning. Situated in Arlington County, Virginia, it houses the leadership and staff of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, Space Force, and associated defense agencies and commands[1]. Originally constructed during World War II as a temporary War Department building, the Pentagon evolved into the permanent nerve center for U.S. military coordination following the 1947 National Security Act, which merged the War and Navy Departments and added the Air Force, establishing the modern DoD[2]. The Pentagon oversees America’s global military posture, playing a crucial role during the Cold War and continuing to adapt to current geopolitical challenges. Its organizational complexity includes civilian oversight through the service secretaries and integration with multinational commands such as NATO and NORAD[1]. The Pentagon is also notable for its vast infrastructure, which underwent a comprehensive renovation completed in the early 2000s to maintain its operational capacity and security[2]. In recent years, the Pentagon has shifted strategic focus to homeland defense and the Western Hemisphere, aligning with contemporary U.S. national security priorities such as border protection and countering adversaries like China[3]. Technologically, it actively invests in emerging industries critical to defense, including space technologies, microelectronics, biochemicals, and software modernization. The Office of Strategic Capital, established to channel private sector investment into defense technologies, exemplifies this focus on innovation and maintaining U.S. technological superiority[4][6]. Efforts such as the Pentagon’s software modernization implementation plan emphasize cloud adoption and agile software development to enhance military IT capabilities[6]. Additionally, political dynamics impact Pentagon leadership and policy directions, as seen in initiatives like Project 2025, which aims to influence personnel and strategic priorities aligned with conservative policy goals[5]. Overall, the Pentagon remains a pivotal institution at the intersection of defense, technology