Israeli Ground Offensive in Gaza Sparks Global Debate

Introduction
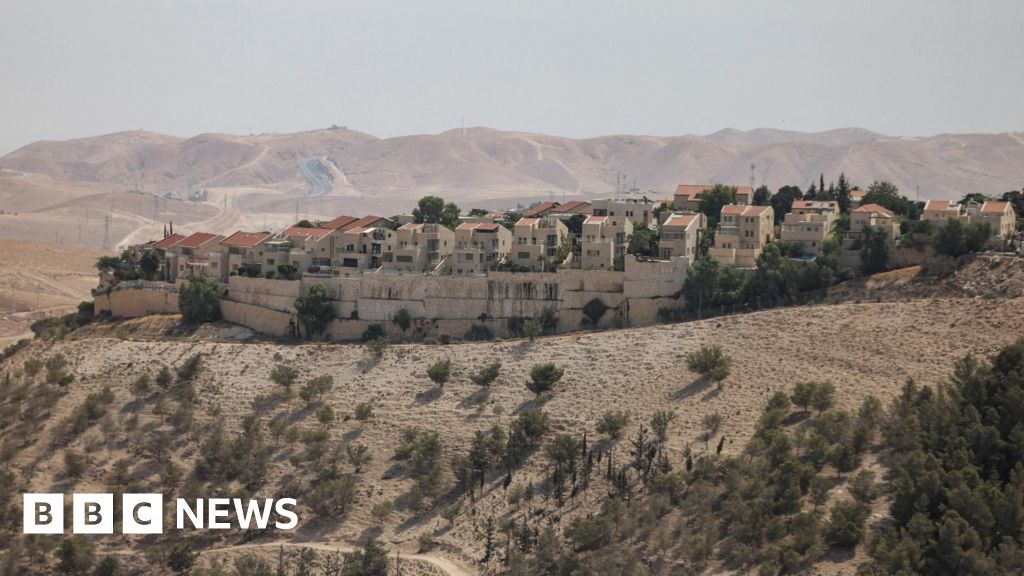
In a controversial move, Israel has launched a ground offensive to occupy Gaza City. This decision has sparked global debate and criticism, with the Trump administration expressing support but also calling for a swift end to the operation.
Key Details
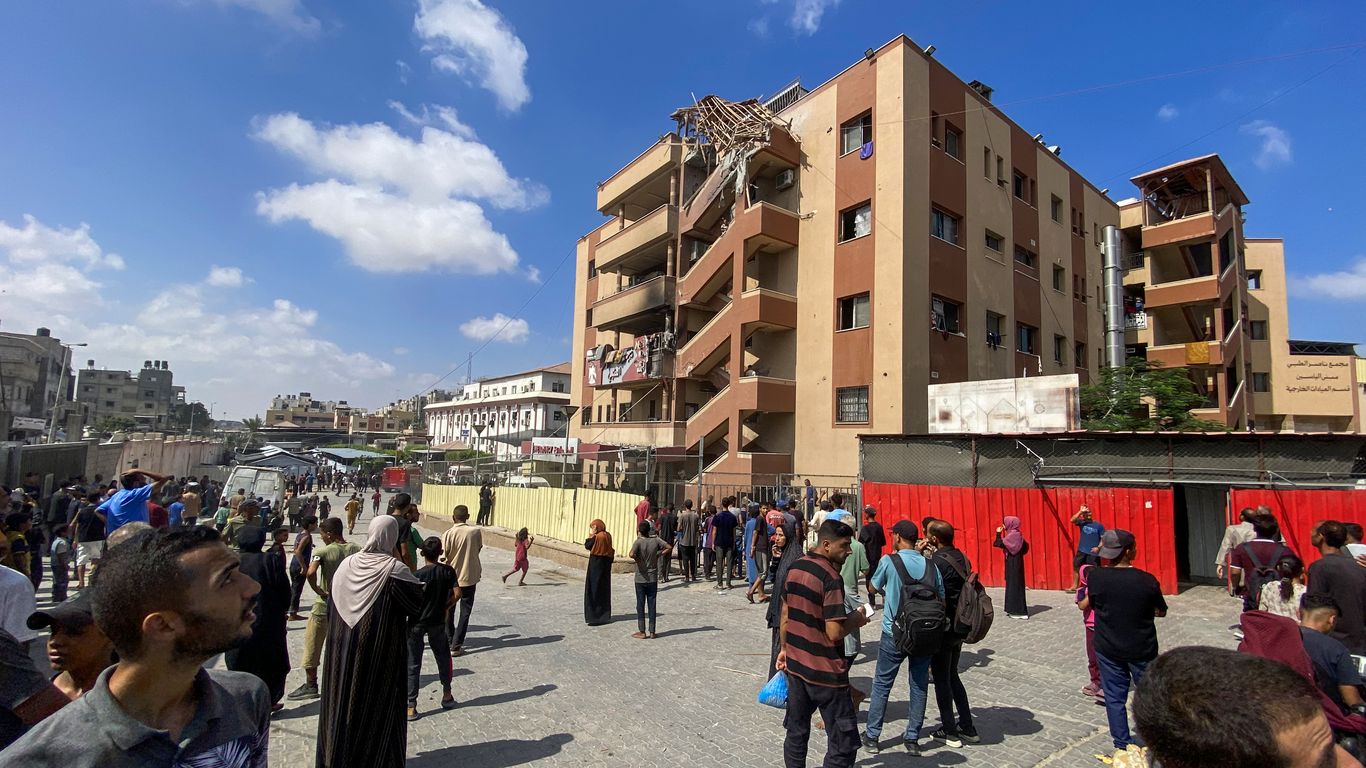
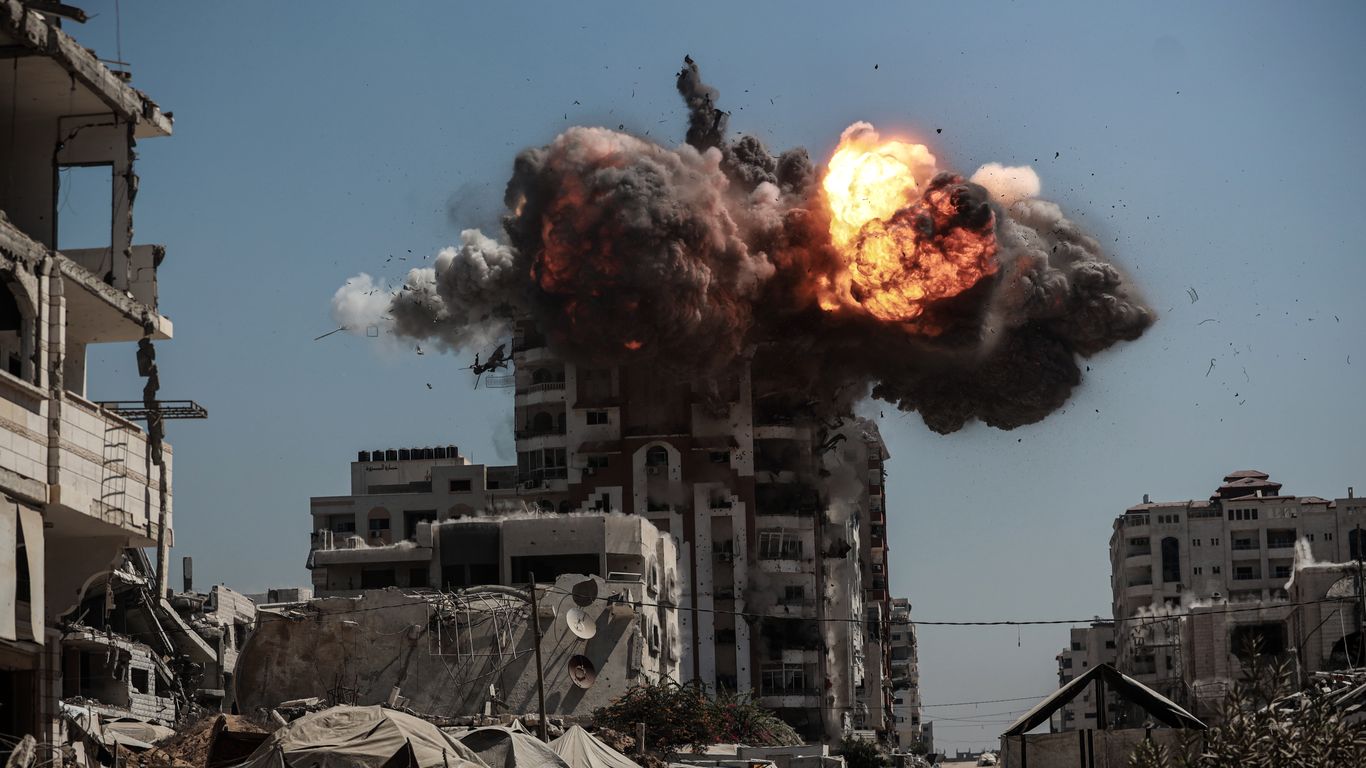
The ground operation follows weeks of escalating tensions between Israel and Hamas, the militant group that controls Gaza. The conflict has resulted in dozens of deaths and hundreds of injuries, with both sides engaging in airstrikes and rocket attacks.
The Israeli government has stated that the ground offensive is necessary to protect its citizens and to eliminate the threat posed by Hamas. However, critics argue that the operation will only further escalate the violence and lead to more civilian casualties.
Impact
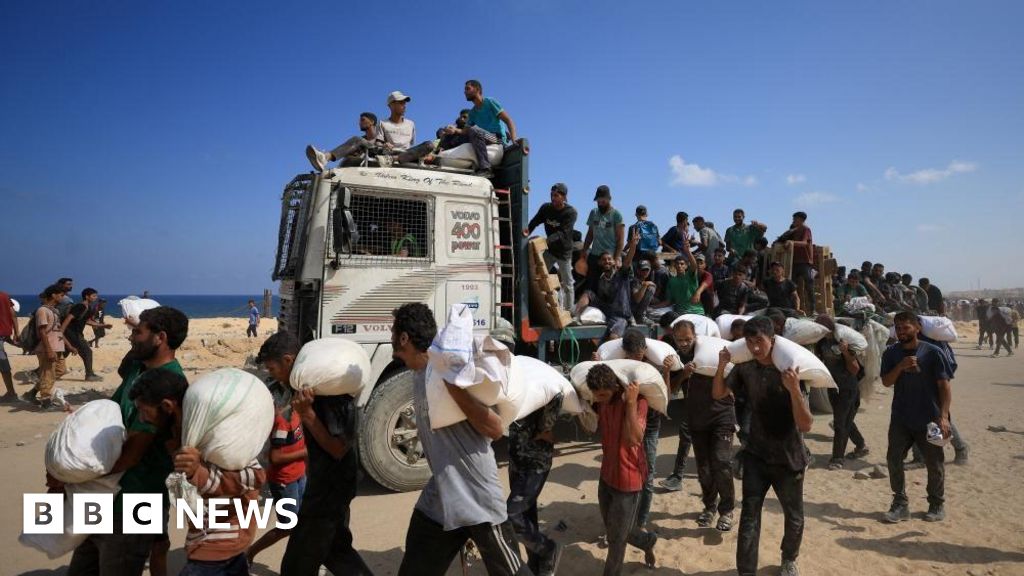
The ground offensive has not only heightened tensions in the region, but it has also sparked international concern. The United Nations has called for an immediate ceasefire, while other countries have urged both sides to find a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
The long-term implications of this operation are yet to be seen. However, it is clear that the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas has far-reaching consequences and must be addressed in a peaceful and diplomatic manner.
About the Organizations Mentioned
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is a pivotal international organization established in 1945, following the devastation of World War II, with the primary goal of maintaining global peace and security, fostering international cooperation, and promoting social progress. The UN Charter, signed by 51 founding member states, including the United States, the United Kingdom, China, and the Soviet Union, laid the foundation for this ambitious endeavor[1][3]. ## History and Structure The UN was born out of the failures of its predecessor, the League of Nations, which failed to prevent World War II. Key planning meetings, such as the Dumbarton Oaks Conference in 1944, defined the UN's structure, which includes the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat[1][6]. The Security Council, with five permanent members (the United States, China, France, Russia, and the United Kingdom), holds significant influence due to its veto power[2]. ## Key Achievements Over the years, the UN has played a crucial role in conflict resolution, human rights advocacy, and sustainable development. Notable achievements include the establishment of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948 and the implementation of numerous peacekeeping missions worldwide[3][4]. The UN has also been instrumental in addressing global challenges such as climate change and pandemics through its various programs and agencies. ## Current Status Today, the UN comprises 193 member states, with its most recent addition being South Sudan in 2011[5]. The organization continues to evolve, addressing emerging issues like digital governance and cybersecurity. Despite challenges, the UN remains a cornerstone of international diplomacy and cooperation. ## Notable Aspects The UN's work is not limited to politics; it also impacts business and technology through initiatives that promote sustainable development and digital inclusion. Its role in setting global standards and fostering international cooperation makes it a significant player in shaping the