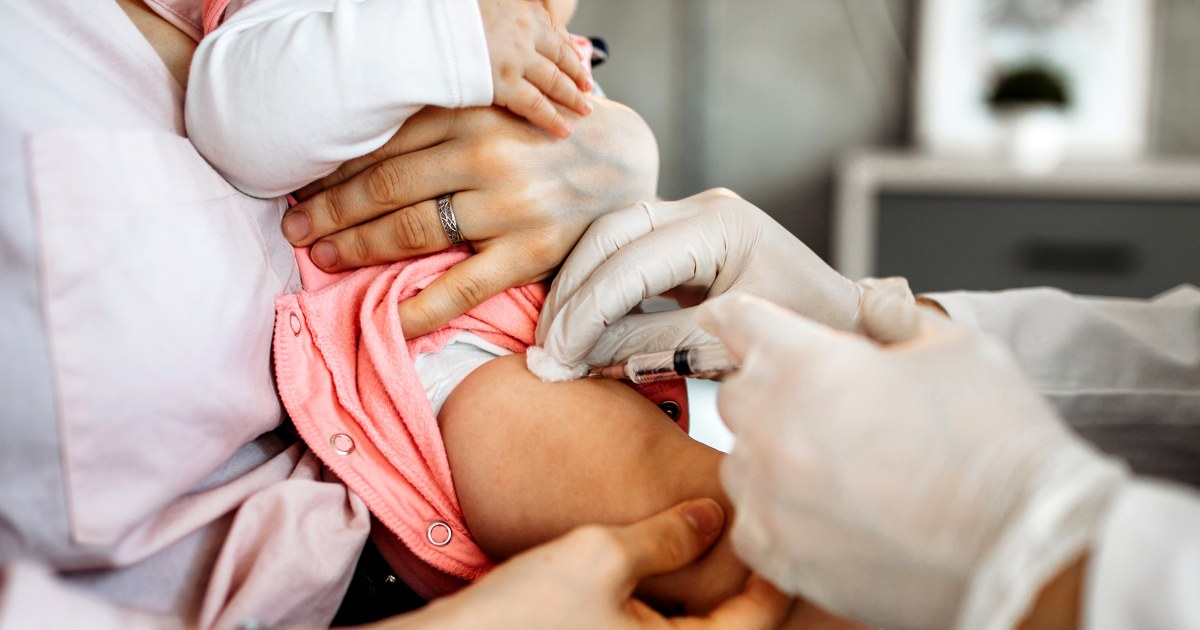
HHS Proposes Overhaul of Childhood Vaccine Schedule to Reduce Injections

HHS announces proposed childhood vaccine schedule overhaul
The Department of Health and Human Services plans a major update to the recommended childhood immunization timetable that aims to reduce the number of shots given to young children and better align U.S. guidance with schedules used in peer countries such as Denmark.
Rationale, changes, and context
Officials say the proposal emphasizes streamlined dosing, fewer early-life injections, and continued protection through revised timing and catch-up options; parents could see longer intervals between some vaccines while public health authorities monitor disease trends and coverage to maintain safety and effectiveness.
Potential impact and next steps
The change could affect pediatric practice patterns, school requirements, and public messaging as agencies solicit expert review and public comment before finalizing a schedule that balances convenience, vaccine uptake, and community immunity goals.
About the Organizations Mentioned
Department of Health and Human Services
## Overview The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government, established to protect the health and well-being of all Americans and to provide essential human services, particularly for those most in need[1][2][4]. With a mission to “enhance the health and well-being of all Americans,” HHS is the principal agency responsible for public health, biomedical research, and the administration of major social welfare programs[1][9]. ## What HHS Does HHS oversees a vast array of programs and services, including direct health care provision, health insurance (Medicare, Medicaid, Children’s Health Insurance Program), public health research, disease prevention, food and drug safety, and emergency preparedness[1][2][5]. The department also funds and supports maternal and child health, early childhood development, substance abuse and mental health services, social services for low-income families, and comprehensive health services for Native Americans[2][7]. HHS works closely with state and local governments, as well as private sector partners, to deliver many of these services[2][3]. ## History HHS traces its origins to the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW), established in 1953. When the Department of Education was created in 1979, HEW was reorganized into HHS, focusing exclusively on health and human services[1][4]. The department has since evolved to address emerging public health challenges, from the HIV/AIDS epidemic to the COVID-19 pandemic[5]. ## Key Achievements - **Medicare and Medicaid:** HHS administers these programs, which provide health insurance to millions of elderly, disabled, and low-income Americans, making it the nation’s largest health insurer[1][2][6]. - **Public Health Leadership:** HHS agencies like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Institutes of Health (NIH), and Food and