Russia Defies Trump's Tariffs: Cuba Oil Sparks Energy Crisis and Geopolitical Tensions

Russia Defies Trump's Tariff Warnings on Cuba Oil
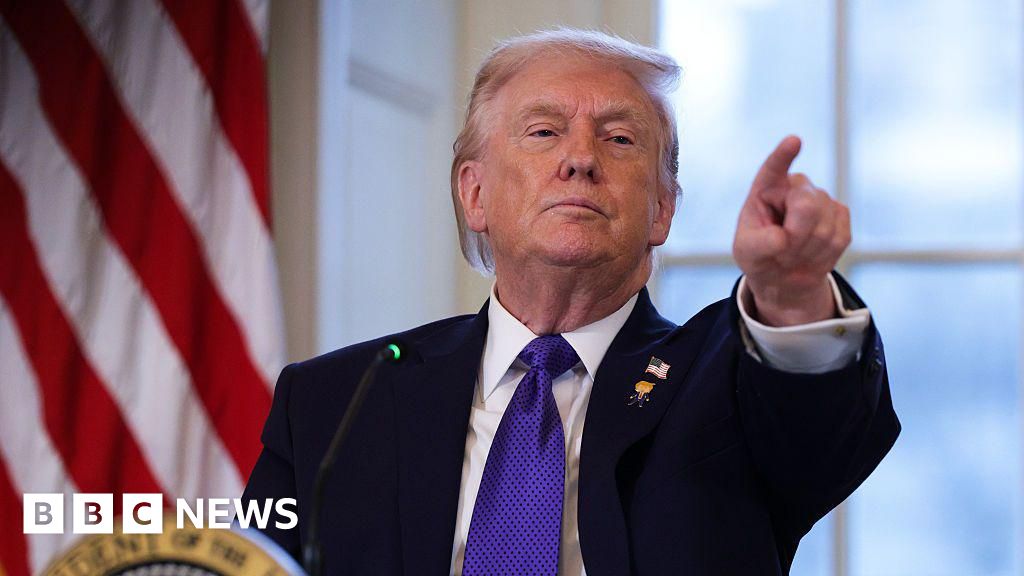
In a bold standoff, Russia dismisses U.S. President Donald Trump's recent tariff threats aimed at nations supplying oil to Cuba. Following Executive Order 14380 on January 29, 2026, which declared a national emergency over Cuba's ties to Russia, China, and Iran, Moscow vows to press on. Labeling Cuba a security threat due to its hosting of Russian intelligence and support for groups like Hezbollah, Trump seeks to choke the island's energy lifeline through secondary tariffs on exporters like Mexico and Venezuela, now halting shipments.
Cuba's Deepening Energy Crisis
Cuba faces blackouts, fuel rationing, and stranded tourists as airlines suspend flights amid jet fuel shortages. Previously reliant on Venezuela for 33% and Mexico for 44% of imports, the nation now eyes Russia's "humanitarian" oil deliveries. Local production falls short of 100,000 daily barrels needed, prompting solar initiatives and prioritized food region supplies—yet reserves dwindle fast.
Geopolitical Ripples Ahead
Russia's move, despite risks like tanker interceptions and budget strains, underscores enduring Havana-Moscow bonds, including debt forgiveness. As analysts predict collapse or concessions within weeks, this escalates U.S.-Russia tensions, testing global energy trade limits and Latin American diplomacy in a high-stakes power play.
About the People Mentioned
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump, born June 14, 1946, in Queens, New York, is an American businessman, media personality, and politician. He graduated from the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School in 1968 with a degree in economics. In 1971, he took over his family’s real estate business, renaming it the Trump Organization, through which he expanded into building and managing skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. Trump gained widespread fame as the host of the reality TV show *The Apprentice* from 2004 to 2015, which helped establish his public persona as a successful entrepreneur. Trump entered politics as a Republican and was elected the 45th president of the United States, serving from 2017 to 2021. His presidency was marked by significant policy actions including tax cuts, deregulation, the appointment of three Supreme Court justices, renegotiation of trade agreements (notably replacing NAFTA with the USMCA), and a focus on immigration control including border wall expansion. He withdrew the U.S. from international agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the Iran nuclear deal, and engaged in a trade war with China. His administration’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic was criticized for downplaying the virus’s severity. Trump was impeached twice by the House of Representatives—first in 2019 for abuse of power and obstruction, and again in 2021 for incitement of insurrection—but was acquitted by the Senate both times. After losing the 2020 election to Joe Biden, Trump challenged the results, culminating in the January 6, 2021, Capitol riot. He remains a central figure in American politics, having won the 2024 presidential election and returned as the 47th president in 2025, continuing to promote policies aimed at economic growth, border security, and military strength[1][2][3][4].
About the Organizations Mentioned
Hezbollah
**Hezbollah** is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary organization founded in 1982 during the Israeli invasion of Lebanon. It emerged under the influence of Iran’s 1979 Islamic Revolution and has maintained close ties with Iran, which provides significant military and financial support. Hezbollah operates a dual structure: a political wing known as the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc in Lebanon’s Parliament, and a powerful paramilitary wing called the Jihad Council, with an armed force comparable to a medium-sized army[1][2]. Historically, Hezbollah’s key mission has been resisting Israeli presence and influence in Lebanon and the broader Middle East. It fought Israeli forces and their local proxies during the 1980s and 1990s, contributing to Israel’s 2000 withdrawal from southern Lebanon. The group gained further prominence in the 2006 Lebanon War, where it effectively challenged the Israeli military, and it later became actively involved in the Syrian civil war, supporting the Assad regime[1][4]. Hezbollah also supports Palestinian militant factions and aligns closely with Iranian regional goals[4]. Hezbollah is designated as a terrorist organization by the United States and over 60 countries and international bodies, reflecting its involvement in attacks beyond Lebanon, including against U.S. and Israeli interests worldwide. It possesses advanced military capabilities such as precision-guided missiles, air defense systems, and unmanned aircraft, although its capabilities suffered degradation in conflicts from 2023 to 2024[3]. The group’s charismatic longtime leader, Hassan Nasrallah, was killed by Israel in 2024, delivering a significant blow to Hezbollah’s leadership[2][3]. Currently, Hezbollah remains a dominant political force in Lebanon with extensive social services but prioritizes its “resistance” military identity. Despite suffering setbacks in recent conflicts, it continues to receive Iranian backing and plays a strategic role as a regional proxy, balancing local Lebanese politics with broader geopolitical ambitions[5][6]. Its complex role as both a political actor and